Figure 2.
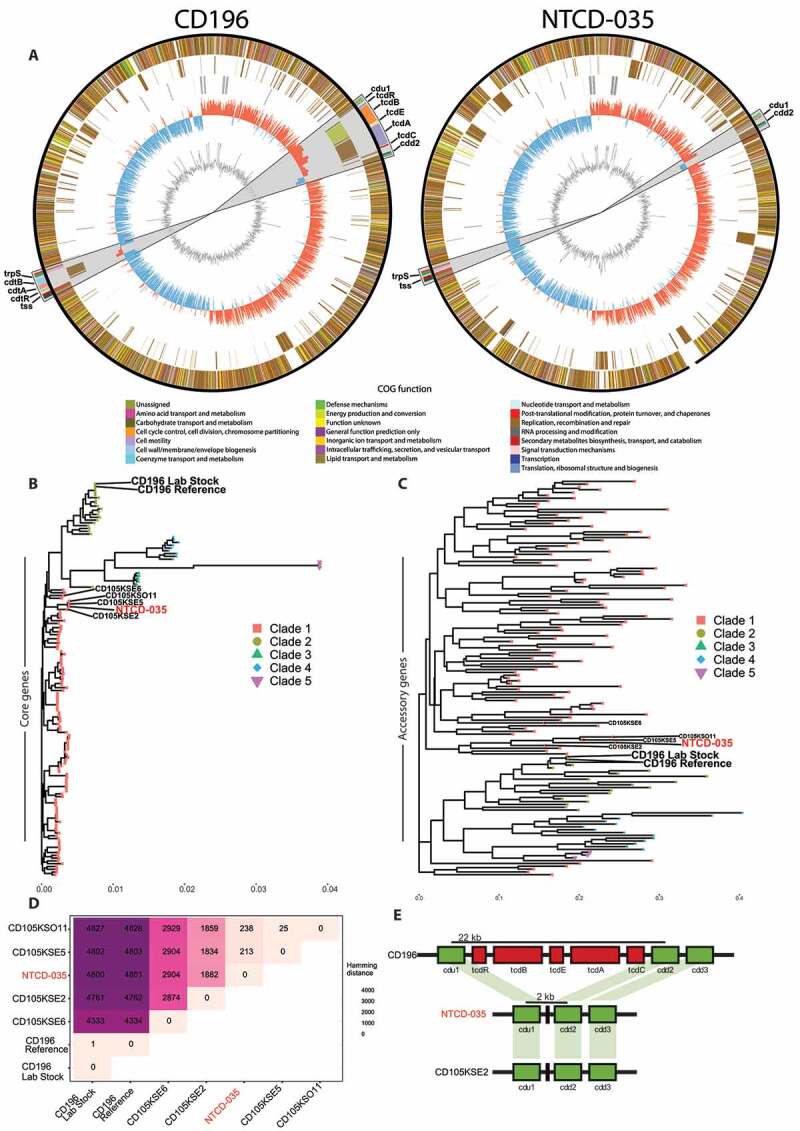
Whole genome sequencing identifies endogenous C. difficile as a novel, non-toxigenic clade 1 member
(a) Circos plots of CD196 and NTCD-035 chromosome contigs. From outside to inside, circles represent shared genes between isolates, unique genes to each isolate, GC skew, and GC content. Color of genes represents annotated gene COG function by Prokka. Grey region 10x zoomed in portion highlighting the region of pathogenicity locus and binary toxin genes. Genomes were rotated with respect to the origin of replication. (b) Phylogenetic analysis of core genes (c) and hierarchical clustering of the presence or absence of accessory genes of C. difficile isolates. (d) Hamming distance of the core genomes between selected C. difficile isolates. (e) Annotated segment of pathogenicity locus comparing distances between cdu1 and cdd2 genes in CD196, NTCD-035, and a similar phylogenetic isolate, CD105KSE2.
