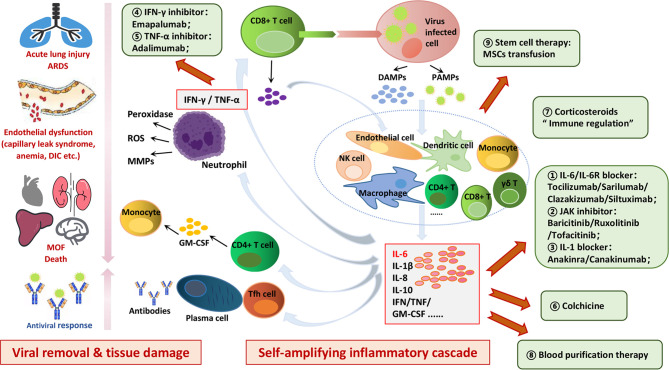
Figure 1.
Mechanisms and hazards of cytokine storms induced in COVID-19 and potential therapeutic targets. Viral infection can induce antiviral responses in neighboring cells as well as recruit innate and adaptive immune cells, such as macrophages, dendritic cells, T cells, B cells and NK cells, leading to self-amplifying inflammatory cascade in a positive feedback loop manner. Cytokine storm not only limits further spread of virus in the body but also induces secondary tissue damage through the secretion of a large number of active mediators and inflammatory factors. The successive occurrences of acute lung injury, abnormal alterations in vascular hemostasis, and cytokine-mediated tissue damage can eventually result in MOF. Potential therapeutic targets to control cytokines storms in COVID-19 are as follows: IL-6/IL-6R blocker; JAK inhibitor; IL-1 blocker; IFN-γ inhibitor; TNF-α inhibitor; colchicine; corticosteroids; blood purification therapy; stem cell therapy.