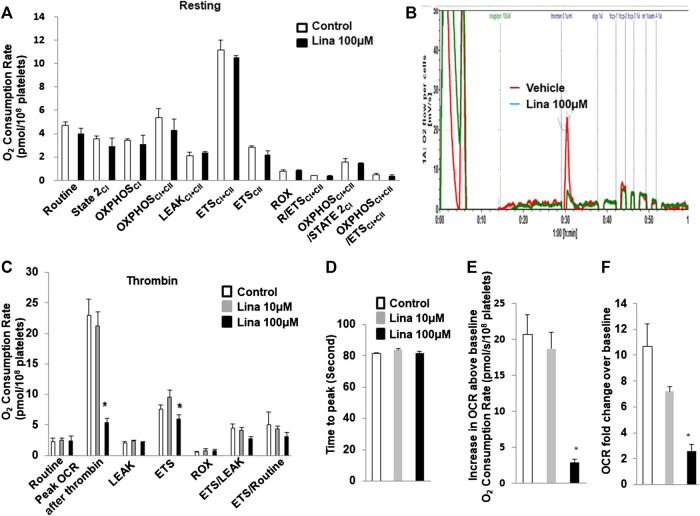
FIGURE 3.
Thrombin promotes an increase in oxygen consumption rate (OCR), which is inhibited by linagliptin. Washed platelets were pretreated with linagliptin (100 μM) or vehicle (DMSO, 0.1%; “control”) for 10 min and then stimulated with thrombin (0.1 U/ml) for 5 min in an Oxygraph-2k high resolution respirometer. (A). Resting platelets were assayed for oxygen consumption after linagliptin treatment; (B) Representative trace showing the typical pattern of OCR and depicting the basal level, proton leak, maximal respiration and reserve capacity after pretreatment with linagliptin (100 μM) for 10 min and stimulation with thrombin (0.1 U/ml) for 5 min (C). Platelets were assayed for oxygen consumption under thrombin-stimulated conditions. Time to peak (D), increase in OCR baseline (E), and OCR fold change over baseline (F) are shown. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n = 3/each group. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle. CI, Complex I-linked substrates; CI + II, Complex I + II-linked substrates; ETS, maximal electron transfer system capacity; ROX, residual oxygen concentration; LEAK, leak-state respiration (non-ADP-stimulated respiration); OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation capacity (ADP-stimulated respiration).