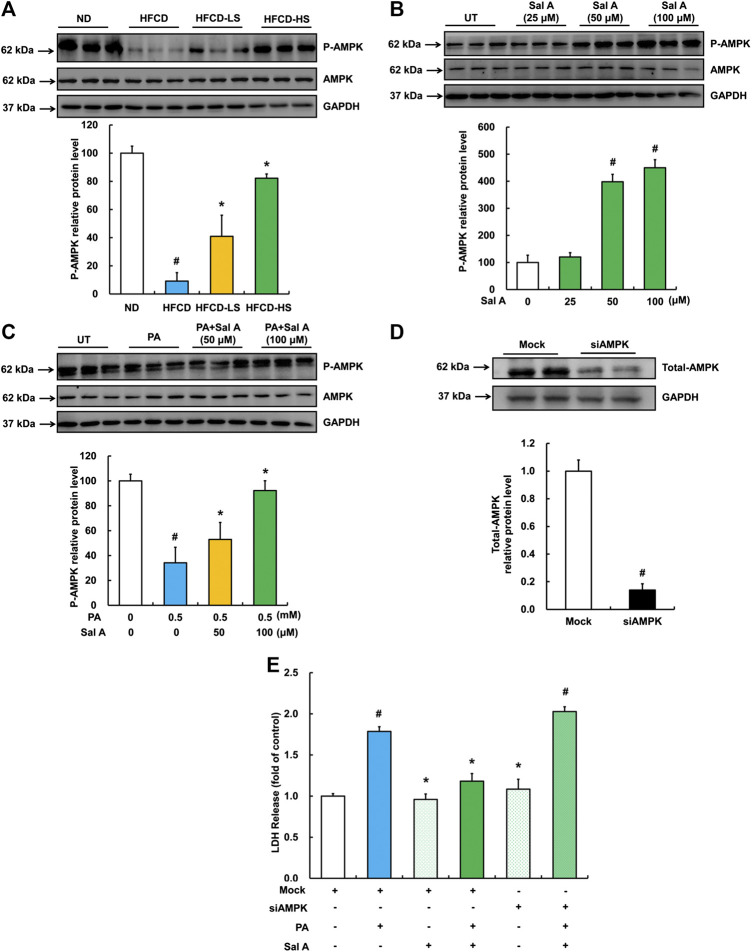
FIGURE 5.
Sal A-activated AMPK contributed to the protection against lipotoxicity-induced liver injury. (A) Total cellular lysates were extracted from mice liver tissues. Immunoblotting was performed for p-AMPK. (B) Cells were treated with different doses of Sal A (25, 50, and 100 μM) for 12 h p-AMPK was detected. (C) HepG2 cells were exposed to 0.5 mM palmitic acid (PA) for 12 h with or without 2 h pre-incubation of Sal A (50 and 100 μM). p-AMPK was detected. (D) HepG2 cells were transfected with siRNAs for AMPK. Silencing efficiency was detected by Immunoblotting assay for AMPK expression. (E) After siRNA silencing of AMPK, cells were exposed to 0.5 mM PA for 12 h with or without 2 h Sal A (100 μM) pretreatment. LDH release was detected. All values are denoted as means ± SD from 12 animal liver samples per group (n = 12) or at least three independent batches of cells. The values with different superscripts are significantly different at p < 0.05. # Comparisons with normal diet (ND) or normal control group; * Comparisons with HFCD group or singly PA treatment group.