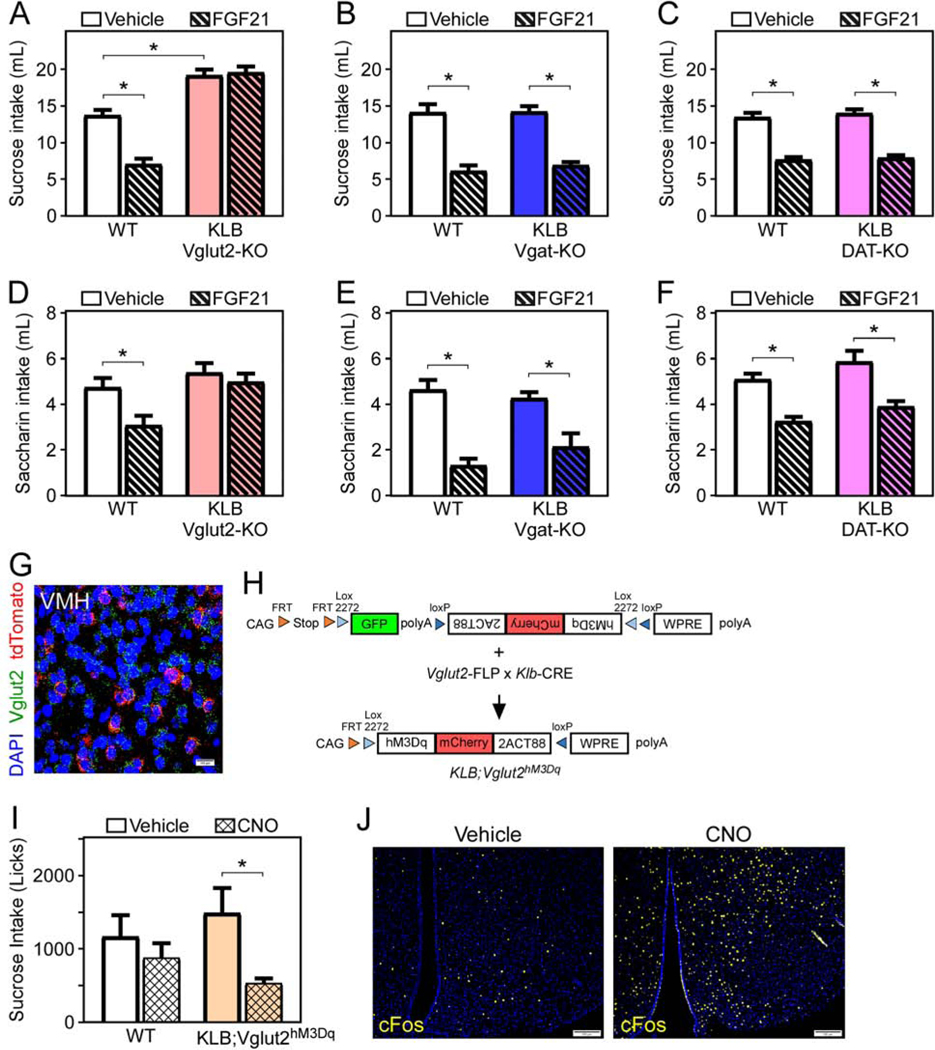
Figure 2. FGF21 signaling to glutamatergic neurons is necessary and sufficient for FGF21-mediated suppression of sucrose intake.
(A-C) Fluid intake during two bottle choice of 10% sucrose versus water in 11–13 week old male WT mice or mice lacking KLB in (A) Vglut2- (KLB Vglut2-KO), (B) Vgat- (KLB Vgat-KO), or (C) DAT-expressing cells (KLB DAT-KO) while receiving daily injections of vehicle (3 days) followed by daily injections of FGF21 (1 mg/kg; 3 days) via i.p. injection (n = 11–21/group).
(D-F) Fluid intake during two-bottle choice of 0.2% saccharin versus water in 11–13-week-old male WT and (D) KLB Vglut2-KO, (E) KLB Vgat-KO, and (F) KLB DAT-KO mice while receiving daily injections of vehicle (3 days) followed by daily injections of FGF21 (1 mg/kg; 3 days) via i.p. injection (n = 7–17/group).
(G) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) demonstrating co-localization of Vglut2 (green) and tdTomato (red) in the ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) of Klb-CRE;Ai14 tdTomato mice.
(H) Schematic representation of the generation of KLB;Vglut2hM3Dq triple knock-in mice. CAG, CAG promoter coding sequence; FRT, FRT sequence; LoxP, LoxP sequence; GFP; green fluorescent protein; hM3Dq-mCherry; excitatory DREADDs construct; WPRE, gene enhancer sequence; polyA, polyadenylation.
(I) Fluid intake (licks) during two-bottle choice of 10% sucrose intake versus water assessed using a lickometer in 11–13-week-old WT and KLB;Vglut2hM3Dq male mice treated with vehicle or clozapine-n-oxide (CNO) (1 mg/kg) via i.p. injections for 3 days (n = 6–8/group).
(J) Immunofluorescence imaging for cFos in the VMH of WT and KLB;Vglut2hM3Dq following 1-hour treatment with CNO.
Values are mean +/− SEM. (*, P < 0.05 compared to WT). Statistical analyses were conducted using 2-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons. Scale bars, 100μm.