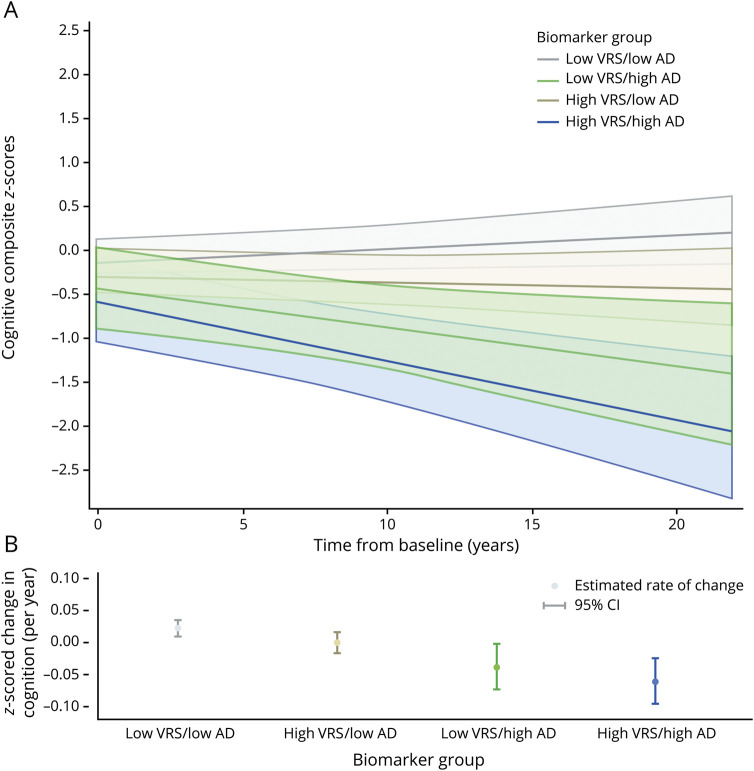
Figure. Estimates of longitudinal cognitive change based on the composite vascular risk score (0 vs ≥1) and AD biomarker group defined by Aβ1-42 and t-tau (low vs high; see text for details).
(A) Adjusted estimates from linear mixed-effects models predicting cognitive composite scores (95% confidence interval [CI]) over time. (B) Adjusted estimates of annual rate of change in cognitive composite scores (95% CI). Predicted marginal rates of global cognitive change were as follows: low vascular risk score (VRS)/low Alzheimer disease (AD) biomarker group estimate 0.022 (95% CI 0.010–0.035); high VRS/low AD biomarker group estimate 0.000 (95% CI −0.016 to 0.016); low VRS/high AD biomarker group estimate −0.038 (95% CI −0.073 to −0.002); and high VRS/high AD biomarker group estimate −0.060 (95% CI −0.096 to −0.024). Corresponding rates of global cognitive change for the CSF biomarker indicator based on β-amyloid1-42 and phosphorylated tau (p-tau) are nearly identical (data not shown). Estimates are adjusted for age, sex, education, APOE ε4 genotype, and their interactions with time. t-tau = total tau.