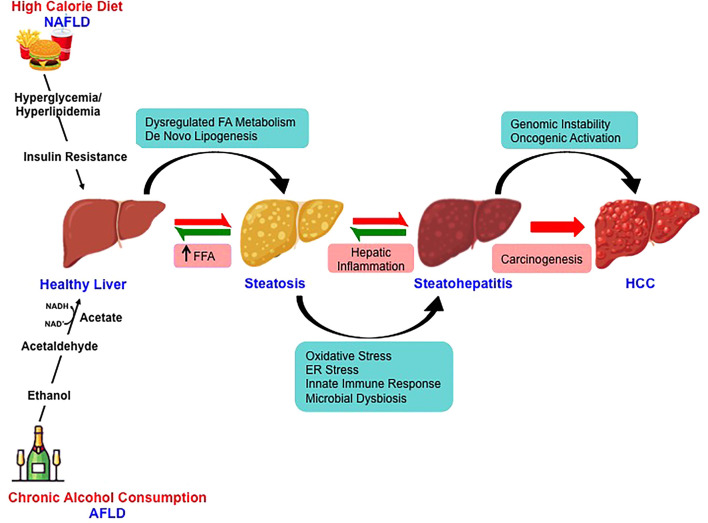
Figure 2.
Molecular mechanisms involved in nonalcoholic- and alcoholic-associated HCC. High-calorie diet and excessive alcohol consumption is the major risk factor for the development of NAFLD and AFLD respectively. Despite the divergent pathogenic origin, the pathological spectra of liver injury in promoting HCC development in NAFLD and AFLD share common molecular pathways.