Figure 1. Biosynthesis of PGE2 and its potential dysregulation in AERD.
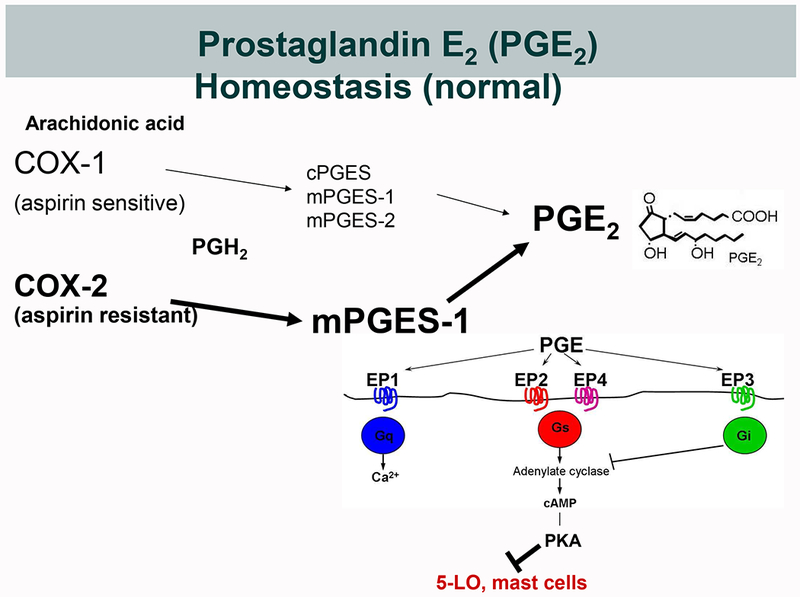
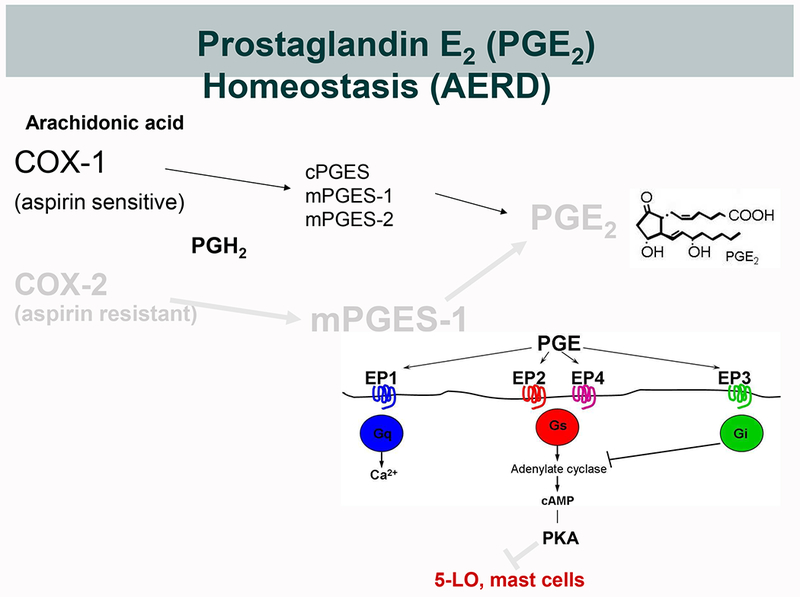
A. Under physiological conditions, PGE2 derives from either constitutively expressed COX-1 or inducibly expressed COX-2. COX-derived PGH2 can be converted to PGE2 by three different terminal PGE2 synthase (PGES) enzymes; cytosolic (c)PGES, and microsomal (m)PGES-1 and -2. During inflammation, the concomitantly induced expressions of COX-2 and mPGES-1 markedly increase the production of PGE2. Because COX-2 is much less sensitive to aspirin than is COX-1, this increase is relatively resistant to low dose aspirin. PGE2 elicits signaling through EP receptors 1-4. EP2 and EP4 activate the cAMP/PKA pathway that stabilizes MCs and blocks leukotriene formation by phosphorylating 5-LO. B. In AERD, the impaired expression and function of the COX-2/mPGES-1 system renders PGE2 production disproportionately dependent on COX-1 and susceptible to inhibition by low dose aspirin. The effects of PGE2 depletion is potentiated by diminished EP2 receptor expression, leading to unbraking of MCs and 5-LO.
