Fig. 2. UBE3A deletions increase BK channel function in human neurons.
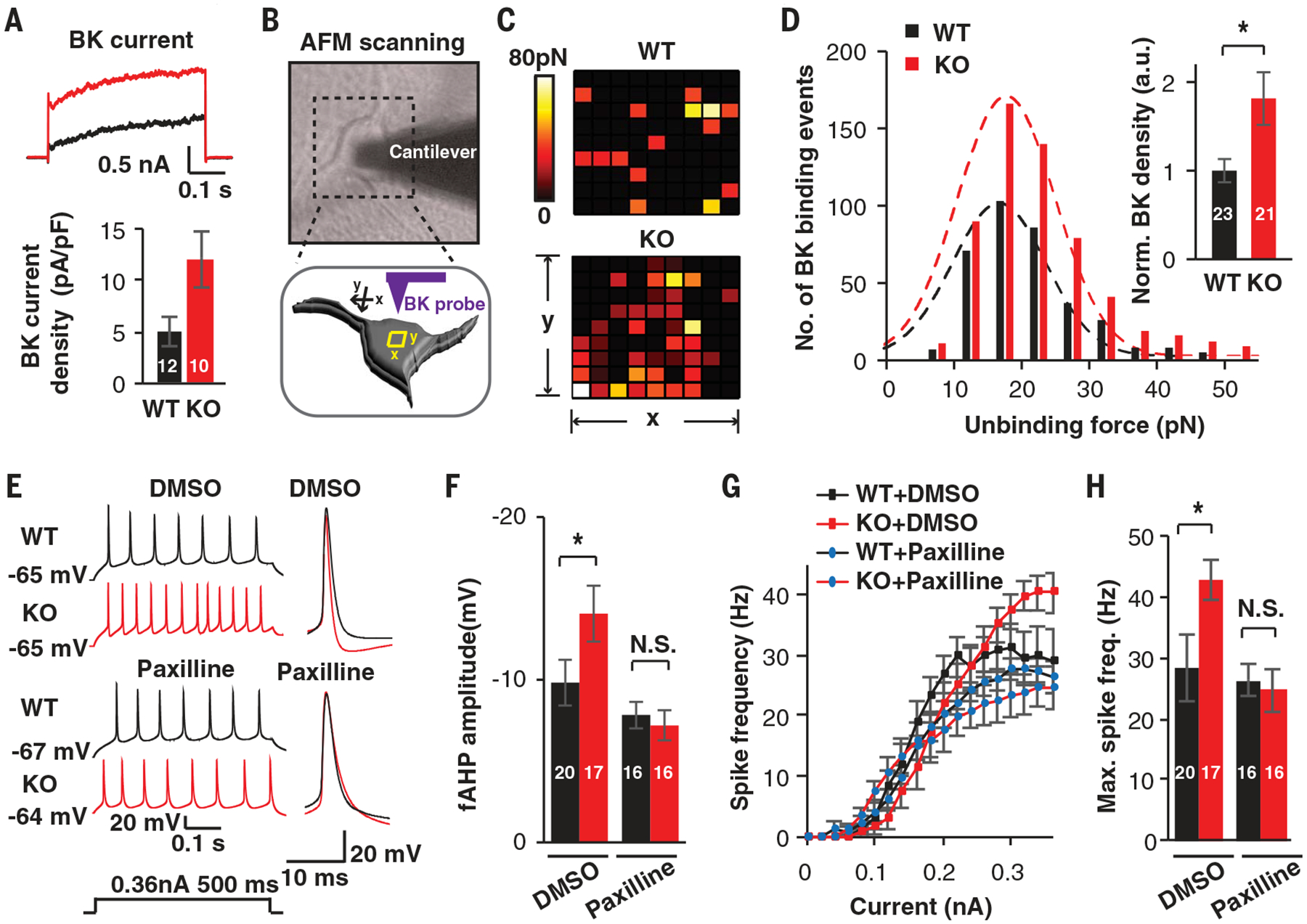
(A) Representative traces and quantification of BK currents isolated from WT and KO neurons treated with paxilline (5 μM). (B) Diagrams illustrating the detection of BK channels using a functionalized probe with AFM. (C) Representative heatmaps of specific BK probe binding events. Force-distance curves (10 data points by 10 data points) were obtained over 1-μm2 areas. Colors indicate the measured force of specific binding events. (D) Unbinding force distribution and BK channel density on the surface of WT and KO neurons. (E to H) Pharmacological rescue by the BK antagonist paxilline. (E and F) Representative traces and quantification of fAHP with and without paxilline (5 μM). DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. (G and H) F-I curves showing spike frequencies versus current injections and related quantification in induced neurons. Data represent means ± SEM. In all bars, the values indicate the number of analyzed neurons. The two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test was used. *P < 0.05; N.S., not significant.
