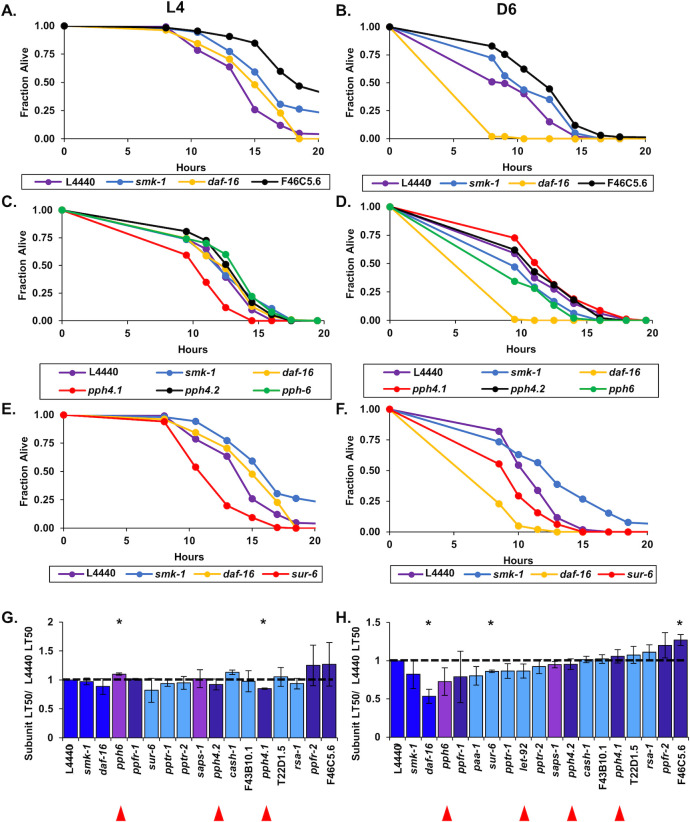
Fig 6. The PP2A subunit SUR-6 contributes to thermotolerance in adult worms.
RNAi treatment targeting C. elegans homologs of catalytic and regulatory subunits of the PP4 (A-D), PP6 (C and D), and PP2A (E and F) complexes was initiated at the L1 stage and continued for the duration of the assay. To induce thermal stress at the L4 larval stage (A,C,E) or at D6 of adulthood (B,D,F) worms were shifted from 20˚ C to 35˚ C until all of the animals had died. The fraction of worms alive at each time point during the incubation at high temperature is plotted as a function of time in hours. In all cases RNAi targeting daf-16 or smk-1 and the empty RNAi vector L4440 were included as controls. Only RNAi knockdowns that produced statistically significant phenotypes are shown. (G and H) The average relative median survival (LT50) of animals treated with RNAi targeting the indicated genes following the shift to 35˚ C at L4 (G) or D6 (H) is shown as a fraction of the average median survival of L4440 controls. Bars, standard error of the mean (SEM). Bar colors correspond to the protein phosphatase complex to which products of the indicated genes belong or to controls. Dark blue: L4440, daf-16, and smk-1; light blue: PP2A; dark purple: PP4; light purple: PP6. Asterisks indicate RNAi treatments producing statistically significant differences in median survival (p<0.05). Horizontal lines are drawn at a relative median survival of 1. Red arrowheads are beneath the names of genes encoding catalytic subunits of the PP2A, 4 and 6 complexes.