Fig 9. Proposed identity of PP2/4/6 complexes in C. elegans and their functions during aging.
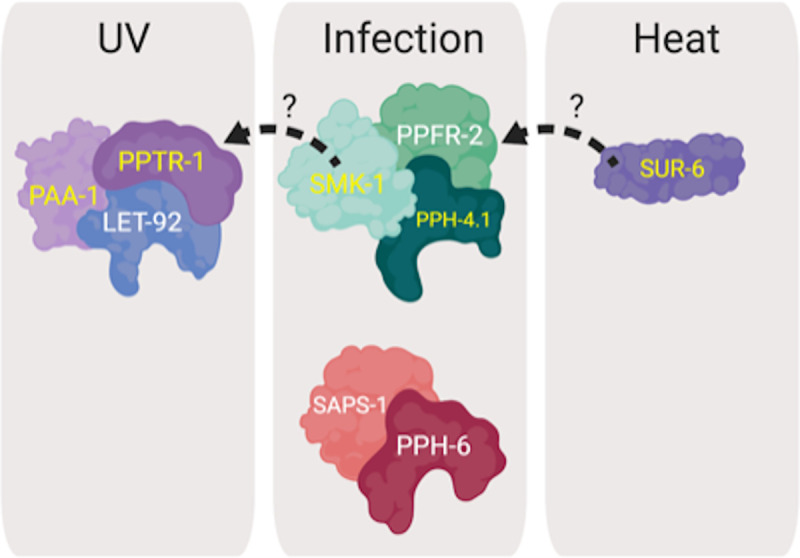
Our data support the existence of at least three central phosphoprotein phosphatase complexes during aging in C. elegans, but different combinations of subunits allow for more. Different versions of the PP2/4/6 complexes could exist in the same cells simultaneously. Alternatively, the composition of the complexes may be dynamic such that individual regulatory subunits associate and dissociate according to cellular demands or in response to external stimuli. The subunit composition of each complex of the PP2/4/6 family in adult C. elegans is indicated, according to the following color scheme: purple, PP2A subunits; green, PP4 subunits; red, PP6 subunits. Proteins whose names are labeled in yellow text are required for the age-dependent increase in DAF-16 transcriptional activity as measured in our in vivo reporter assay. While the PP2A complex is important for resistance to UV light, both the PP4 and PP6 complexes function in innate immunity in adult worms. Subunit exchange (indicated by dashed arrows) may take place between constituents of the PP2A and PP4 complexes such that SMK-1 associates with a version of the PP2A complex to confer resistance to UV irradiation and SUR-6 associates with PP4 to contribute to host defense. SUR-6 was the only PP2A/4/6 family member found to play a role in thermotolerance during adulthood. Protein structures depicted in this cartoon are for illustrative purposes only.
