Figure 1.
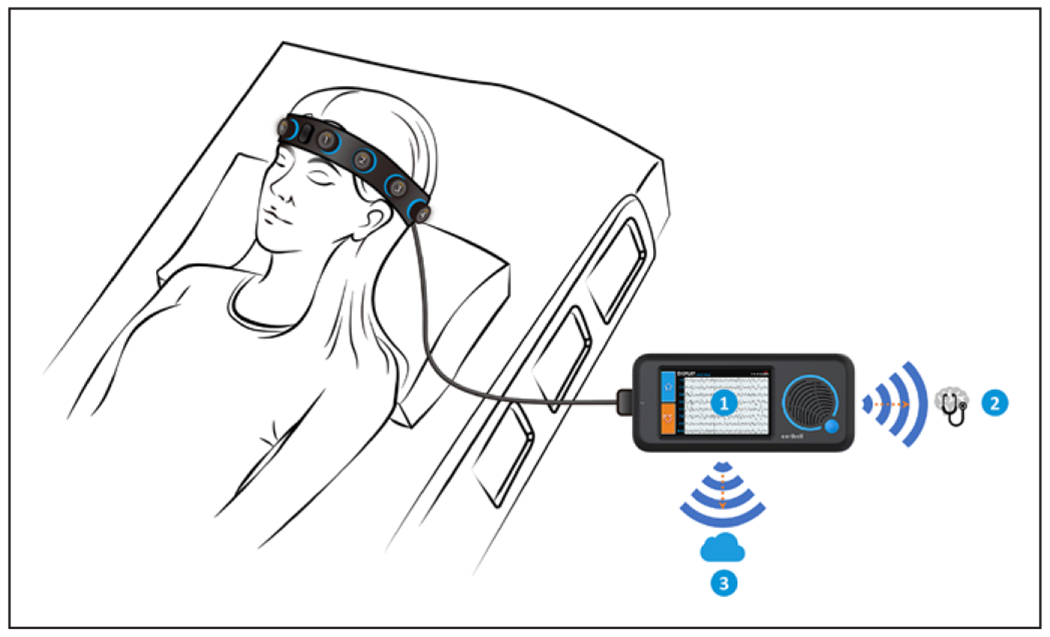
Rapid Response Electroencephalogram (Rapid-EEG) System. Rapid-EEG developed by Ceribell enables electroencephalogram (EEG) acquisition without trained EEG technologists and provides EEG diagnostic information in real time by three means: 1) the visual display on the device screen, 2) the “Brain Stethoscope” (38) function activated by a button press on the device that enables the user to “listen” to the sound of the brain (for samples, see “Brain Stethoscope Training” at https://ceribell.com/training.html), and 3) real-time wireless transmission of the EEG data to a cloud server for remote evaluation (either in real time or retrospectively) by neurologists using a web browser interface. The electrodes are configured in a bipolar montage with five electrodes (four electrode pairs) on each hemisphere. The EEG channels correspond approximately to the Fp1–F7, F7–T3, T3–T5, and T5–O1 sites on the left and the Fp2–F8, F8–T4, T4–T6, and T6–O2 sites on the right according to the International 10–20 System. Data are acquired as digital samples at a rate of 250 Hz with a frequency response of 0.5–100 Hz.
