Figure 1: Currently recognized mechanisms of lipid acquisition by cancer cells.
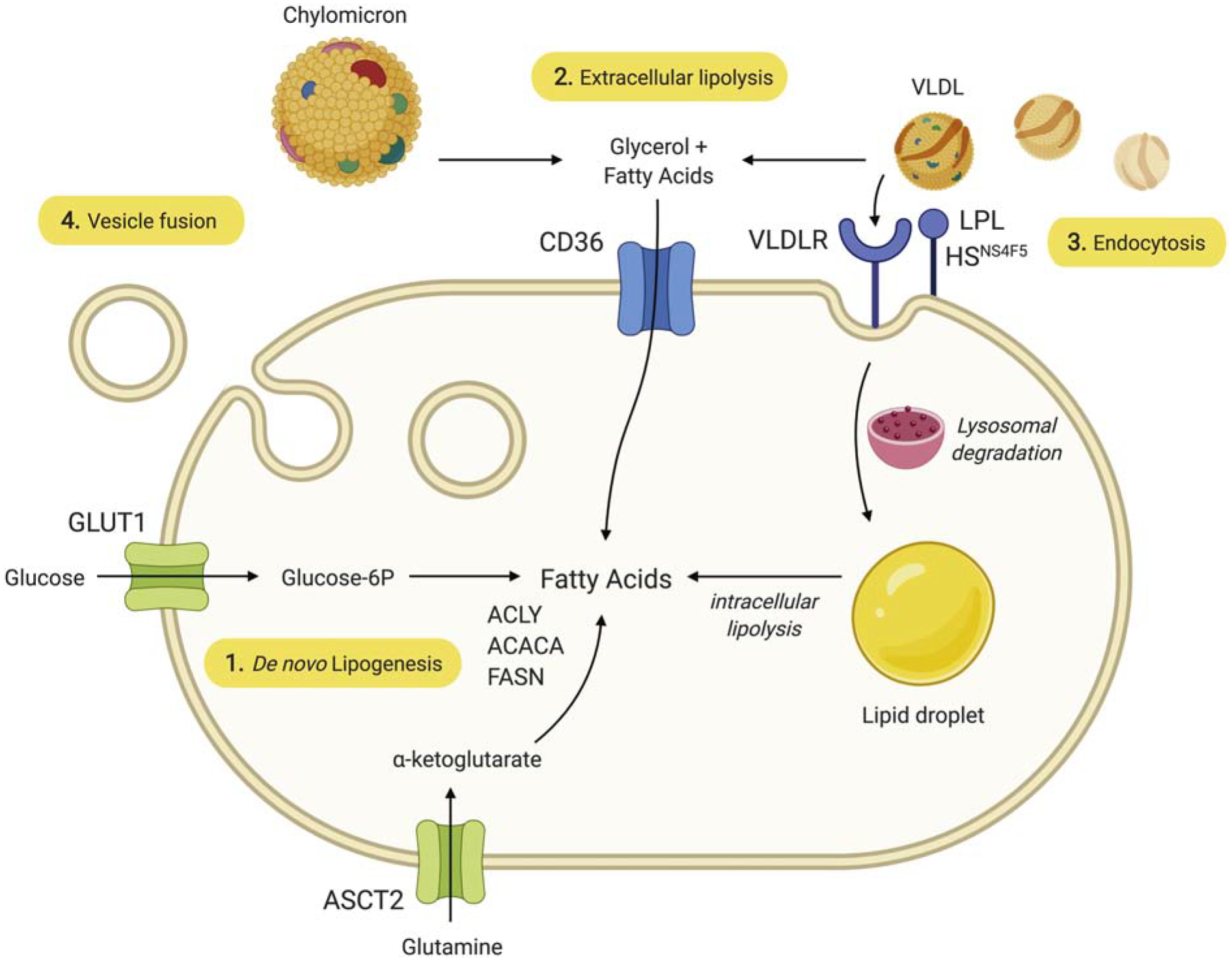
1) FA may be synthesized de novo using ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), acetyl-CoA carboxylase-α (ACACA), and fatty acid synthase (FASN). 2) FFA derived from the circulation or from local LPL-mediated extracellular lipolysis of TAG carried in lipoproteins such as VLDL enter the cell through CD36. 3) Alternatively, VLDL may dock on LPL that is bound to the cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan motif HSNS4F5, which optimizes positioning of the VLDL for endocytosis using the VLDL receptor (VLDLR). In this case, TAG are hydrolyzed intracellularly. Cholesterol-rich LDL particles may be similarly endocytosed using the LDL receptor without participation of LPL or HSNS4F5 (not shown). 4) Lipids and other molecules carried in exosomal vesicles may enter the cell through fusion with the plasma membrane.
