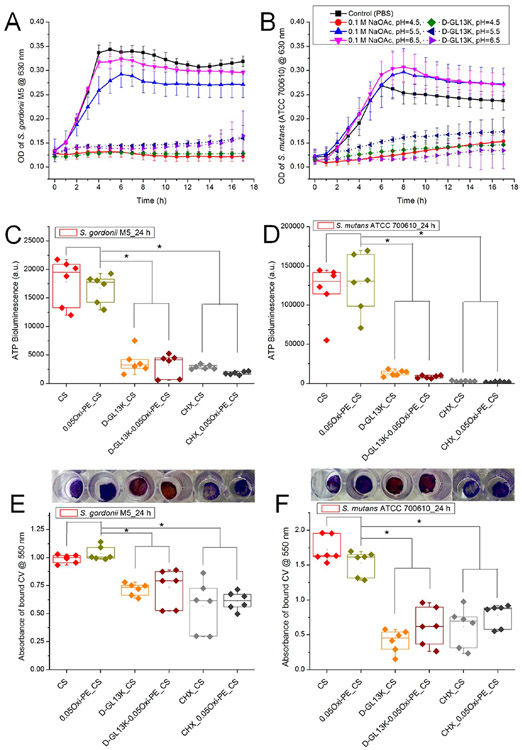
Figure 6.
Indirect assessment of the antimicrobial potency of D-GL13K released from the chitosan membranes under different pH (4.5, 5.5, and 6.5) conditions. The release aliquots from the blank or D-GL13K absorbed membranes were cultured with bacterial suspensions in a 1:1 (v/v) ratio, and growth curves were recorded in the kinetic mode at 1 h intervals for (A) S. gordonii M5 and (B) S. mutans (ATCC 700610). Data shown in the line graphs are means ± standard deviation of n = 3–6 replicates. Direct assessment of (C, E) S. gordonii or (D, F) S. mutans colonization of chitosan-based nanofiber membranes after 24 h of bacterial culture measured by (C, D) ATP bioluminescence assay and (E, F) crystal violet stained biomass/bioburden. Representative macroscopic images of crystal violet stained membranes are shown above the corresponding experimental groups plotted in parts E and F. Each data point represents one replicate, and boxplots present statistical values for each group. * indicates statistical significance (p < 0.05) between the compared groups. CS, chitosan; 0.05Oxi-PE_CS, 0.05 wt % oxidized pectin coated chitosan; D-GL13K_CS, D-GL13K absorbed CS; D-GL13K-0.05Oxi-PE_CS, 0.05 wt % oxidized pectin coating on D-GL13K absorbed CS.