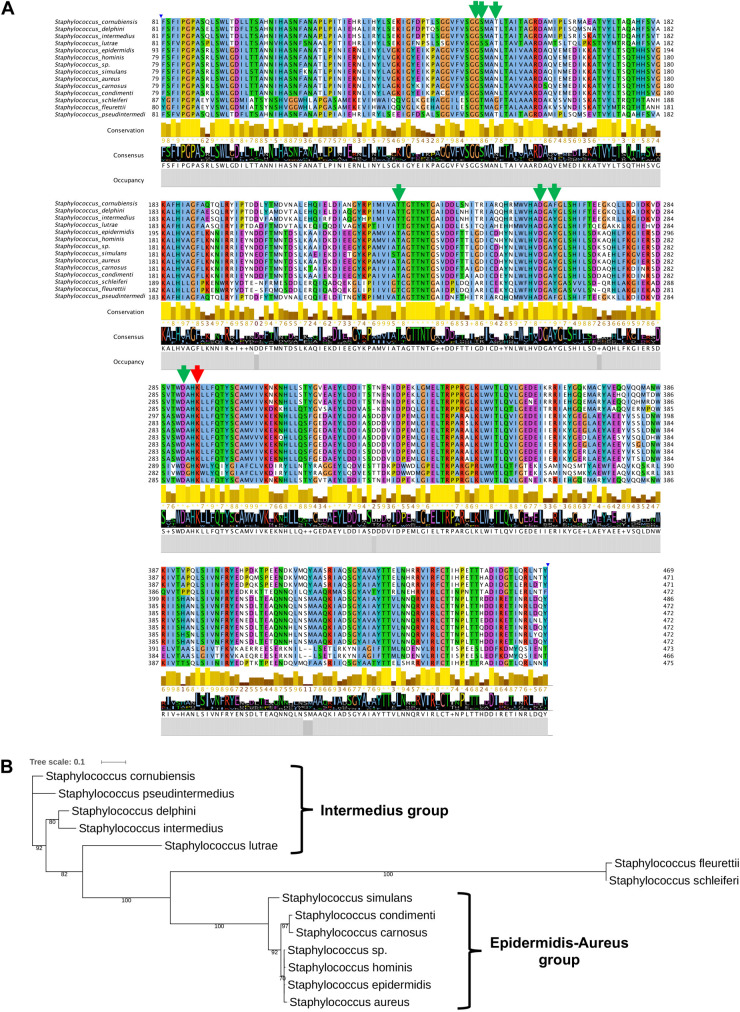
FIGURE 5.
SadA in TA-producing staphylococci is highly conserved. (A) We aligned multiple sequences of the pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent aspartate aminotransferase superfamily (fold I) domain (accession cd06450) of SadA from species within the genus Staphylococcus and visualized using Jalview 2.11 (Letunic and Bork., 2019). The proposed PLP-binding domain (green) of SadA and the catalytic site Lysine (red) are highly conserved. (B) The 475 aa SadA sequence from S. pseudintermedius ED99 (WP_014612792) was used as a reference to identify homologs within the Staphylococcus genus using BLASTP. All best hits were used to construct the phylogenetic tree, using the Randomized Axelerated maximum-likelihood (RaxML) method (version8.2.9) (Sievers et al., 2011). Node support is indicated by bootstrap values from 100 resamplings of the alignment.