Fig. 3 |. EPYC1 binds to Rubisco small subunit α-helices via salt bridges and a hydrophobic pocket.
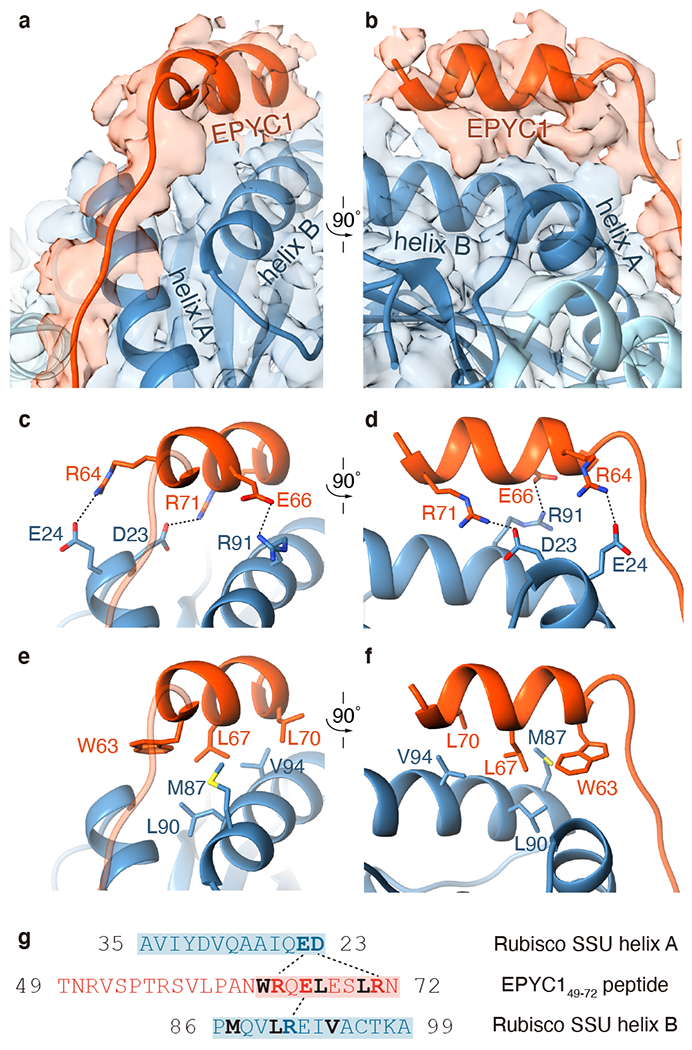
a-b, Front (a) and side (b) views of the EPYC149-72 peptide (red) bound to the two α-helices of the Rubisco small subunit (blue). c-d, Three pairs of residues form salt bridges between the helix of the EPYC149-72 peptide and the helices on the Rubisco small subunit. Shown are front (c) and side (d) views as in panel a and panel b. The distances from EPYC1 R64, R71 and E66 to Rubisco small subunit E24, D23 and R91 are 3.06 Å, 2.78 Å, and 2.79 Å, respectively. e-f, A hydrophobic pocket is formed by three residues of the EPYC149–72 peptide and three residues of helix B of the Rubisco small subunit. Shown are front (e) and side (f) views as in panel a and panel b. g, Summary of the interactions observed between the EPYC149-72 peptide and the two α-helices of the Rubisco small subunit. Helices are highlighted; the residues mediating interactions are bold; salt bridges are shown as dotted lines; residues contributing to the hydrophobic pocket are shown in black.
