Figure 2.
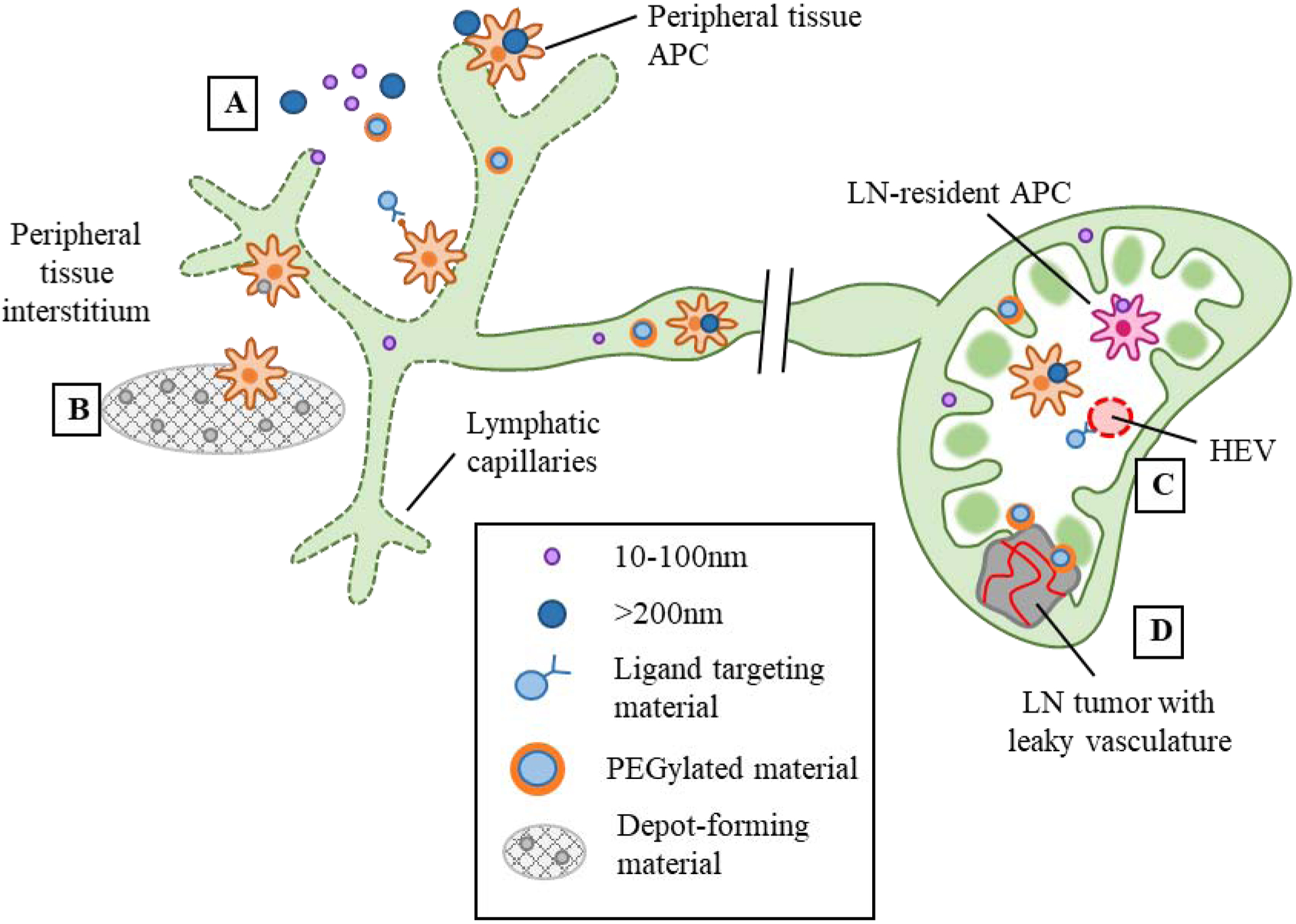
Design strategies for lymphatic-targeting drug delivery systems. A) From the peripheral tissue interstitium, particles sized 10–100nm drain passively via lymphatic capillaries and are taken up via LN-resident DCs, while larger >200nm particles are transported to the LN via peripheral tissue-resident APCs. In addition to size, PEGylation and incorporation of targeting ligands can also enhance lymphatic uptake. B) Depot-forming materials promote peripheral tissue APC infiltration followed by migration to the LN. C) Particles incorporated with high endothelial (HEV)-targeting ligands can enter via the bloodstream. D) Leaky vasculature of LN tumors or metastases may allow particles to enter from the bloodstream.
