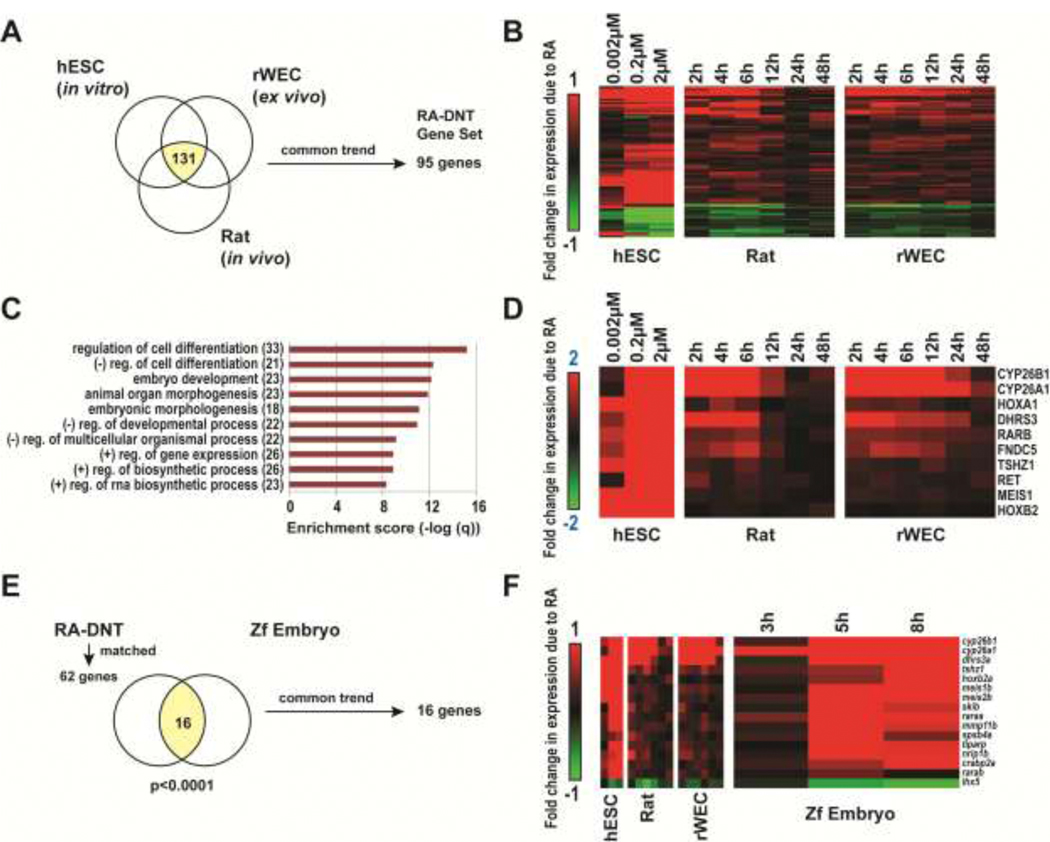
Figure 3. Characterization of common genes identified to be differentially expressed with RA exposure and associated with developmental neurotoxicity in mammalian models.
(A) We identified 131 genes to be commonly differentially expressed in association with DNT across in vitro, ex vivo and in vitro models (p<0.005, ANOVA). (B) Hierarchical clustering of the subset of 95 genes that displayed common trends in regulation, of which 74 were upregulated and 21 were downregulated with RA exposure in a concentration or time-dependent manner. This subset of genes was termed the RA-DNT gene set. (C) Identified enriched GO Biological Processes within the RA-DNT gene set (q<1*10−10). (D) RA-DNT genes with absolute average fold change ≥ 2 (log 2 scale) comparing RA vs. control per study. (E) We identified homologues for 64% (61 total genes) of the RA-DNT gene set. Within this subset, we identified 16 genes to be altered with RA in the Zf embryo model. All 16 genes trended in similar fashion to RA-exposed mammalian model systems. Referenced datasets: E-MEXP-3577 [135], GSE33195 [128], and GSE43755 [154].