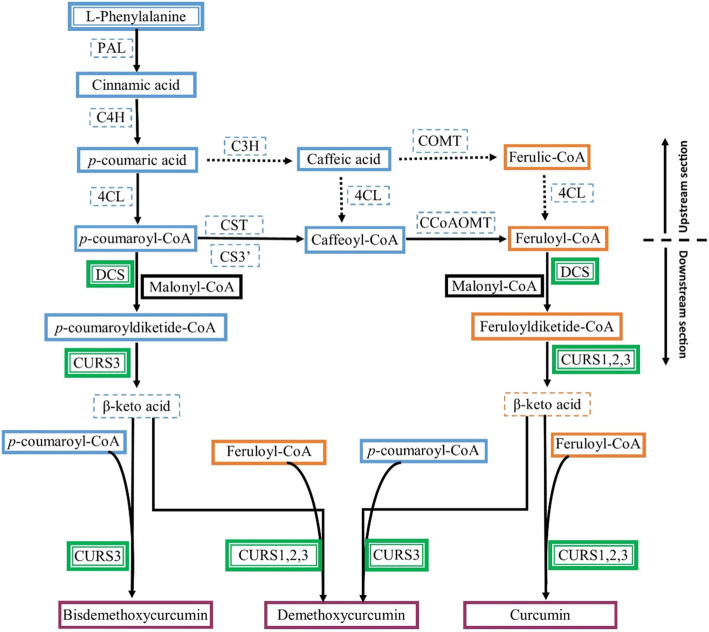
Fig. 4.
Curcuminoid biosynthesis pathway in turmeric [adapted and modified from Ramirez-Ahumada et al. [14] and Katsuyama et al. [19, 20]]. Cinnamic acid is synthesized from phenylalanine by phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) and converted into coumaric acid by cinnamate-4-hydroxylase (C4H). Then, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) converts coumaric acid into coumaroyl-CoA, and p-coumaroyl shikimate transferase (CST), p-coumaroyl 5-O-shikimate 3-hydroxylase (CS3=H), and caffeoyl-CoA-O-methyltransferase (CCoAOMT) convert it into feruloyl-CoA. Coumaroyl-CoA and feruloyl-CoA are then converted by diketide-CoA synthase (DCS) into diketide-CoAs by condensation with malonyl-CoA. In the end, multiple curcumin synthases (CURS1, CURS2, and CURS3) catalyze the formation of curcuminoids by condensing the diketide-CoAs with coumaroyl-CoA and feruloyl-CoA. Depending on the combination, different curcuminoids are produced, namely curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin. The route indicated by solid arrows corresponds to the central phenylpropanoid pathway that occur in vivo, in C. longa