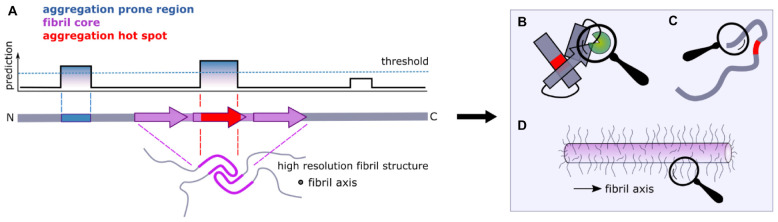
FIGURE 2.
Flanking regions and amyloid formation. (A) Computational approaches can be used to identify aggregation-prone regions (APRs) from sequence data alone (blue). Fibril cores are defined by cryoEM and ssNMR structures of amyloid fibrils and include residues that adopt a stable cross-β structure (purple). When the APRs and the fibril core overlap, we term the region as an “aggregation hotspot” (red). Large segments of a protein sequence can remain dynamically disordered in amyloid structures (lower image). (B) Interaction partners and/or (C) the formation of transient non-local intra-molecular interactions that involve regions that flank the APRs can have significant effects on the aggregation kinetics of amyloidogenic proteins, as well as on their function. (D) Dynamically disordered regions flanking the amyloid core in the fibrillar state form an amyloid “fuzzy coat” that can impart biological functions to the amyloid fold.