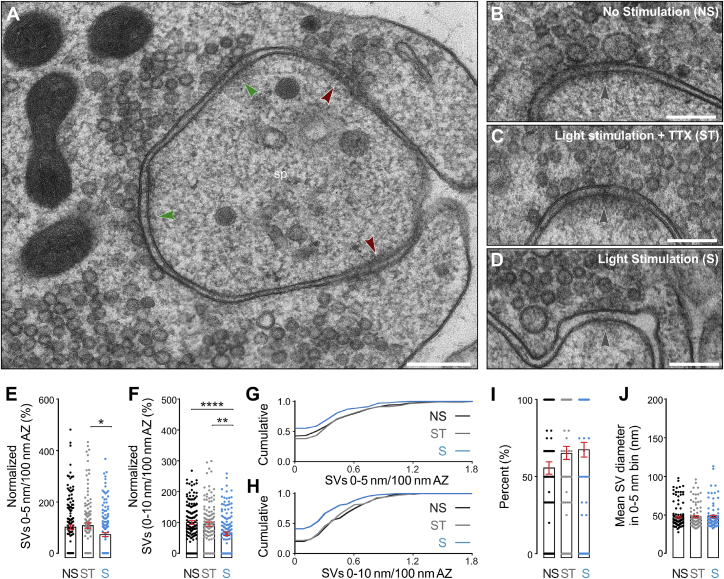
Figure 4.
2D Ultrastructural Analysis of Mossy Fiber Synapses from Dock10-Cre;Ai32 Slices after High-Frequency Stimulation (100 × 5 ms LPs at 20 Hz, 2 mM Ca2+)
(A) Electron micrograph of active zone (AZ) profiles contacting spines (sp). Cross-sections of AZs with defined bilayers (green arrowheads) were analyzed, whereas AZ profiles exhibiting high membrane curvature were excluded (red arrowheads).
(B–D) Electron micrographs of AZs in three experimental conditions: NS, no stimulation (B); ST, light stimulation + 1 μM TTX (C); S, light stimulation (D).
(E and F) Spatial density of vesicles within 0 to 5 nm (E) and 0 to 10 nm (F) of the AZ per 100-nm AZ length. Values are normalized to the NS control condition.
(G and H) Cumulative distribution of vesicles within 0 to 5 nm (G) and 0 to 10 nm (H) of the AZ per 100 nm AZ length.
(I) Relative proportion of all vesicles within 0 to 10 nm of the AZ localized within in the 0 to 5 nm bin.
(J) Mean diameter of vesicles within 0 to 5 nm of the AZ. NS, 136 vesicles; ST, 105 vesicles; S, 94 vesicles.
Scale bars: 200 nm (A–D). Error bars indicate mean ± SEM; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. NS, three cultures, three slices, 47 MFBs, n = 135 AZs; ST, three cultures, three slices, 39 MFBs, n = 114 AZs; S, three cultures, three slices, 38 MFBs, n = 140 AZs.