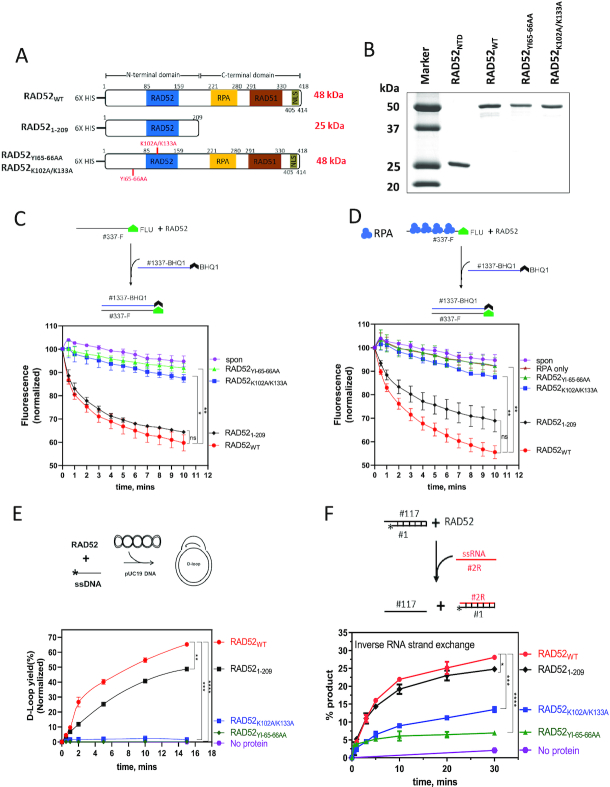
Figure 3.
Characterization of the biochemical activities of RAD52WT, RAD521–209, RAD52YI65–66AA and RAD52K102A/K133A proteins. (A) The scheme of RAD52 constructs similar to Figure 1A except 6× His tag was added at their N-terminus. RAD521–209 contains 1–209 residues., RAD52YI65–66AA and RAD52K102A/K133A are generated by mutating Y65/I66 and K102/K133 to alanine residues, respectively. (B) A 15% SDS-PAGE gel of purified proteins (1 μg each) stained with coomassie blue. Molecular weight markers shown in lane 1. (C and D) Top: the scheme of the ssDNA annealing assay without (C) and with RPA (D). Fluorescently labeled ssDNA (no. 337-F; 0.5, nM molecules) was pre-incubated with RPA dilution buffer (C) or RPA (1 nM) (D). RAD52WT (10 nM), RAD521–209 (40 nM), RAD52YI65–66AA (10 nM) or RAD52K102A/K133A (10 nM) was then added to the reaction, followed by addition of complimentary ssDNA carrying a quencher (no. 1337-BHQ; 0.5 nM molecules). Bottom: the kinetics of ssDNA annealing. (E) Top: the scheme of the D-loop assay. The asterisk denotes 32P-label. RAD52WT (450 nM), RAD521–209 (800 nM), RAD52YI65–66AA (450 nM) or RAD52K102A/K133A (450 nM) was incubated with ssDNA (no. 160; 3 μM, nucleotide) followed by addition of supercoiled pUC19 dsDNA (50 μM, nucleotide) Bottom: the kinetics of D-loop formation. (F) Top: the scheme of inverse RNA strand exchange. Asterisk represents 32P-label. RAD52WT (900 nM), RAD521–209 (1.4 μM), RAD52YI65–66AA (900 nM), RAD52K102A/K133A (900 nM) was incubated with the 3′-tailed DNA (no. 1/no. 117; 68.6 nM molecules) followed by addition of RNA (no. 2R; 205.8 nM molecules). Bottom: the kinetics of inverse RNA strand exchange. Oligonucleotide sequences for C, D, E and F are shown in Supplementary Table S1. Error bars indicate S.E.M. (n = 3) and statistical analysis was performed using Two-way ANOVA with Dunnette's multiple comparison test; ns P > 0.05, *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 and ****P ≤ 0.0001. Significance shown for last time-point in C, D, E and F.