Figure 4.
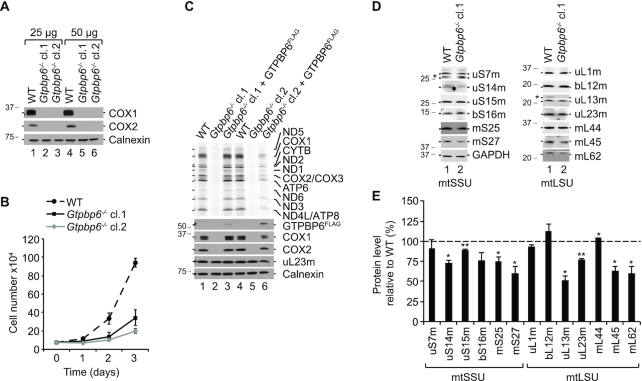
GTPBP6 is essential for mitochondrial gene expression. (A) Loss of GTPBP6 inhibits synthesis of mtDNA-encoded proteins. Cell lysates from HEK293T-wild type (WT) and Gtpbp6−/− cells were analyzed by western blotting using antibodies as indicated. Two clones obtained from CRISPR/Cas9 application followed by FACS were used, indicated as cl.1 and cl.2. (B) Ablation of GTPBP6 affects cell growth. HEK293T-wild type (WT) and Gtpbp6−/− cells were seeded into 6-well plates using DMEM media and counted after 1 d, 2 d and 3 d (n = 3; mean ± SD). The growth rate of Gtpbp6−/− clone 1 and clone 2 was estimated to be reduced by 1.8- and 2.5-fold, respectively compared to WT. (C) Essential role of GTPBP6 in translation of mtDNA-encoded proteins. HEK293T-wild type (WT), Gtpbp6−/− and Gtpbp6−/− cells inducibly expressing GTPBP6FLAG were analyzed by [35S]Methionine de novo incorporation. Samples were analyzed by autoradiography and western blotting, respectively. (D) The effect of GTPBP6 ablation on synthesis of mitoribosomal proteins. Cell lysates from HEK293T-wild type (WT) and Gtpbp6−/− cells (cl. 1) were analyzed by western blotting using Typhoon imaging system (GE Healthcare). (*) indicates unspecific signal. GAPDH was used as loading control. (E) Relative protein levels were quantified from (D) using ImageQuant TL software. The expression level of tested proteins in wild type cells are marked as dashed line (100%) (n = 3; mean ± SEM; * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01).