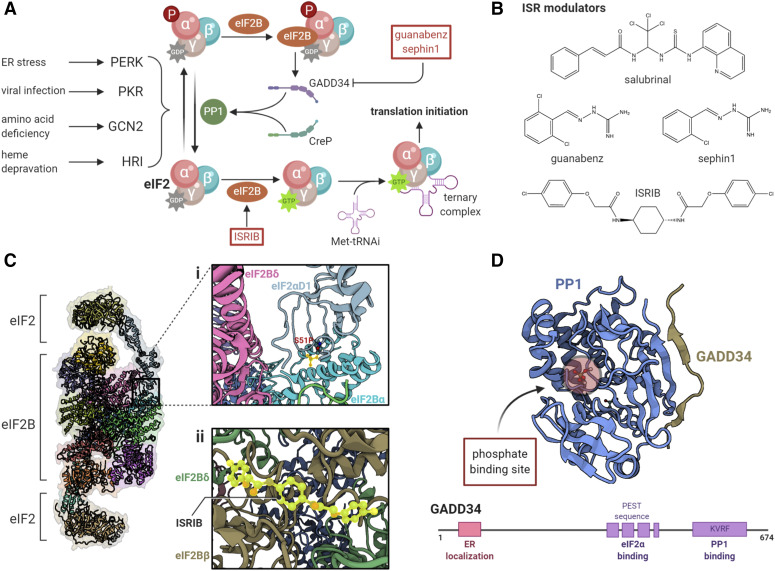
Fig. 2.
Modulation of the integrated stress response. (A) The ternary complex, consisting of GTP-bound eIF2 and the initiator Met-tRNAi, aids in the recognition of the start codon. The GTP bound to eIF2 is hydrolyzed upon encountering the start codon. The resulting GDP-eIF2 dissociates from the initiation complex and is recycled by eIF2B for the next round of initiation. Under cellular stress, four kinases (PERK, PKR, GCN2, and HRI) phosphorylate eIF2α at Ser51 and initiate the ISR, which inhibits global translation by sequestering available eIF2B. (B) Various small molecules are known to modulate the ISR, particularly by maintaining phosphorylation of eIF2α (e.g., salubrinal, guanabenz, and sephin1) or by activating eIF2B (e.g., ISRIB). (Ci) Phosphorylation of eIF2α stabilizes the interaction of two molecules of eIF2 with eIF2Bα and eIF2Bδ subunits of eIF2B, inducing a conformational rearrangement that prevents the GDP to GTP exchange and competes with the binding of Met-tRNAi. In this manner, phospho-eIF2α acts as a noncompetitive inhibitor of eIF2B [Gordiyenko et al. (2019), PDB: 6QG0]. (Cii) ISRIB restores eIF2B levels by facilitating the binding of two tetramer subunits, particularly by interacting with eIF2Bδ and eIF2Bβ [Zyryanova et al. (2018), PDB: 6EZO]. (D) Although phosphorylation of eIF2α suppresses global translation, it induces the expression of certain genes, such as ATF4, CHOP, and GADD34. GADD34 is a stress-induced regulatory subunit of PP1, which dephosphorylates phospho-eIF2α to normalize translation. Recent structural and functional analysis shows that GADD34 promotes binding of PP1 and phospho-eIF2α via its lysine (K), valine (V), arginine (R), and phenylalanine (F).(KVRF) and proline (P), glutamic acid (E), serine (S), and threonine (T) (PEST) motifs, respectively [Choy et al. (2015), PDB: 4XPN]. The PEST sequences in GADD34 are not found in CreP, a constitutively active PP1 regulatory subunit, and may represent a novel target for the suppression of ISR-induced GADD34.