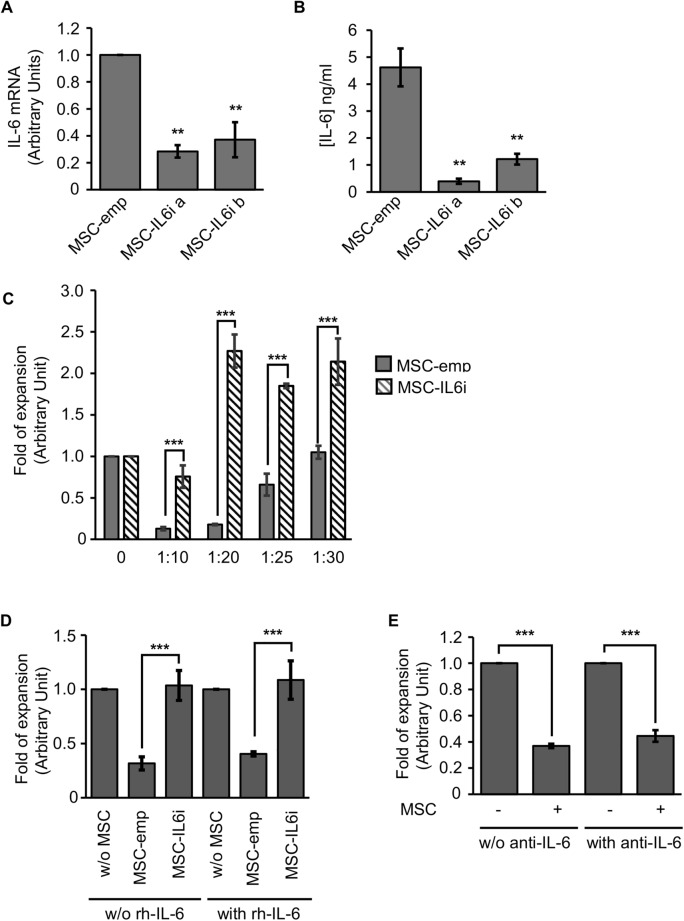
Figure 2.
IL-6 is involved in hMSC-mediated inhibition of activated T-cell proliferation. (A) Quantification of IL-6 expression by real time qPCR. Graphs represent mean values of three independent experiments, and error bars represent the mean ± SD of the experiments. The expression levels of the target gene were normalized against GAPDH expression. **p < 0.01. (B) Quantification of IL-6 secretion using a CBA kit. Graphs represent mean values of three independent experiments, and error bars represent the mean ± SD of these experiments. **p < 0.01. (C) Proliferation of T-cells cultured in the absence of hMSCs (0), co-cultured with hMSC-emp or hMSC-IL6i using different ratios of hMSCs/T-cells. Data are shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. ***p < 0.001. (D) Proliferation of T-cells cultured in the absence of hMSCs, (w/o), co-cultured with hMSC-emp or hMSC-IL6i in the absence (w/o) or presence of recombinant IL-6 (20 ng/ml). Data are shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. (E) Proliferation of T-cells cultured in the absence of hMSCs or co-cultured with hMSC, in presence or absence (w/o) of a blocking anti-IL6 antibody (5 μg/ml). Data are shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. **p < 0.01.