Figure 1. . Clearance of rabies virus from the CNS depends on blood–brain barrier permeability and immune cell infiltration.
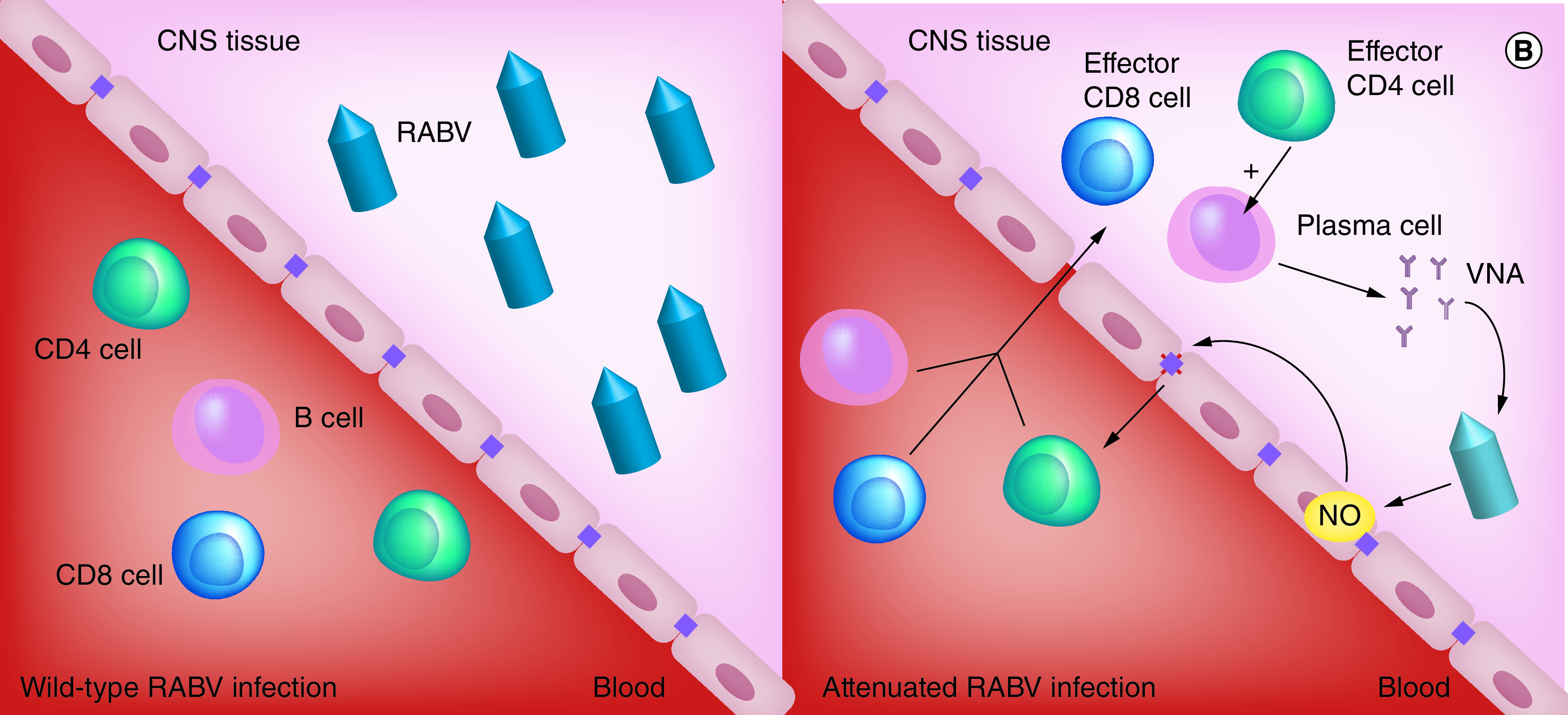
(A) Wild-type RABV travel by axonal retrograde transport from the infection site to the CNS, thereby leaving the BBB intact and preventing the infiltration of immune effectors. (B) Infection with an attenuated virus leads to the BBB’s permeabilization, allowing the recruitment of immune effectors to the CNS. The cooperation of CD4+ cells and B cells induces VNA and clearance of the virus.
BBB: Blood–brain barrier; EC: Endothelial cell; NO: Nitric oxide; RABV: Rabies virus; VNA: Virus neutralizing antibody.
