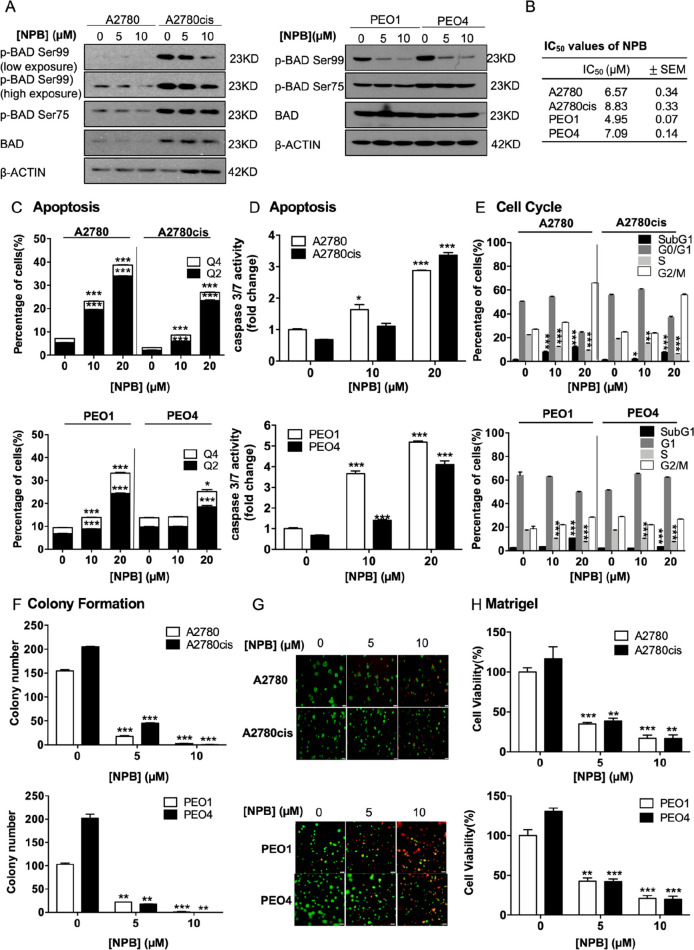
Figure 2.
NPB stimulates apoptosis and reduces cell cycle progression in both cisplatin-sensitive and -resistant ovarian cancer cells. (A) Levels of phosphorylated and total BAD after 24 h of treatment with NPB in A2780, A2780cis, PEO1, and PEO4 cells were determined by Western blot analysis. β-ACTIN was used as input control. (B) IC50 values of NPB after 72 h of treatment in both cisplatin-sensitive and-resistant EOC cell lines were determined by the AlamarBlue cell viability assay. (C) Apoptotic cell death was determined after 24 h of NPB treatment by flow cytometry in both cisplatin-sensitive and -resistant EOC cell lines. Q4: Early apoptotic population (PI–, FITC-Annexin V+). Q2: Late apoptotic population (PI+, FITC-Annexin V+). (D) Apoptosis of NPB treated cells was determined using Caspase 3/7 assay 24 h post-treatment. (E) Cell cycle progression in the cell lines after 24 h of treatment with NPB was determined using flow cytometry. (F) Colony formation was performed in respective cell lines with treatment of NPB. The cells were allowed to grow for 10 days for A2780/A2780cis and 14 days for PEO1/PEO4 before the number of colonies were counted under a microscope. (G) Cells were cultured in 2% FBS medium containing 4% Matrigel for 3 days prior to treatment with NPB for 6 days. Live cells were stained by calcein (green color) and dead cells were stained by PI (red color), scale bar: 200 μm. (H) Viability of cells grown in 3D Matrigel were determined using AlamarBlue cell viability assay. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.