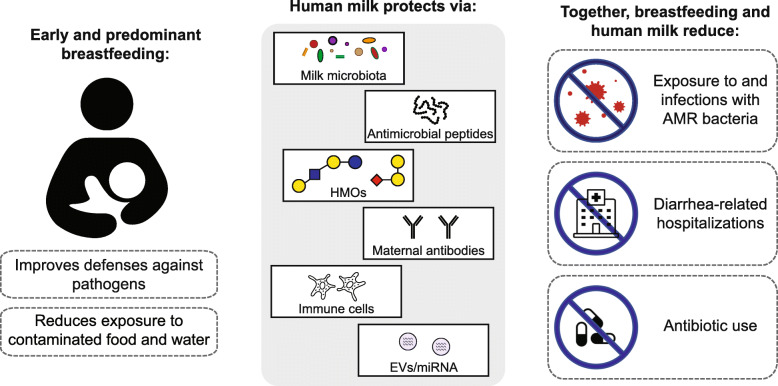
Fig. 2.
Ways breastfeeding and human milk could prevent the establishment, proliferation, and/or selection of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria among young children. Exclusive or predominant breastfeeding for an extended duration improves children’s defenses against pathogens and reduces their food- and waterborne exposures to antimicrobial-resistant bacteria. Human milk contains multiple components that could protect against antimicrobial-resistant pathogens and reduce the lateral transfer of antibiotic resistance genes. The concentrations of some of these components are highest in colostrum, the earliest form of human milk. HMOs, human milk oligosaccharides; EVs, extracellular vesicles; miRNA, microRNA; AMR, antimicrobial resistance