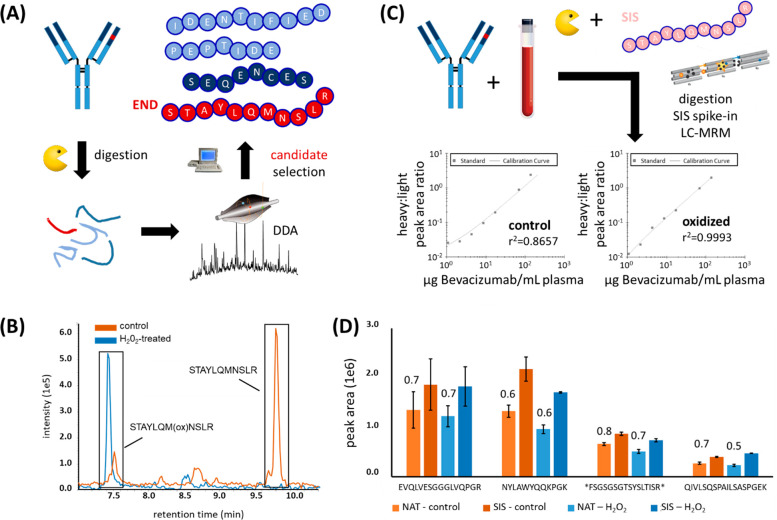
Figure 1.
Bevacizumab quantitation using the Met-containing peptide STAYLQMNSLR. (A) Bevacizumab was digested using trypsin and analyzed by data-dependent acquisition (DDA) to identify proteotypic peptide candidates that can be used for an MRM-based assay. The Met-containing peptide STAYLQMNSLR showed the highest response during LC-MS. (B) STAYLQMNSLR either treated with (blue) or without H2O2 (orange), analyzed on a Sciex TripleTOF 6600 (AB Sciex). Extracted ion chromatograms of the oxidized (∼7.5 min) and nonoxidized (∼9.7 min) forms are shown, indicating the presence of both variants in the nontreated sample, while the nonoxidized variant was completely absent upon treatment with H2O2. (C) Bevacizumab was spiked at different concentrations into human plasma, followed by proteolytic digestion, addition of SIS peptide as normalizer, and analysis by LC-MRM (left: no oxidation, right: oxidation with H2O2). (D) Non-Met-containing control peptides are not significantly affected by H2O2 treatment. Light (NAT) peptides representing various mAbs were spiked into plasma and treated with (blue) or without H2O2 (orange), followed by addition of SIS peptides and LC-MRM analysis. n = 3. H2O2 oxidation did not considerably alter precision, nor did it considerably change the peak area ratios of corresponding NAT/SIS pairs. These ratios are indicated above the respective NAT peptide peak area bars. Error bars represent standard deviations. * = peak area × 10.