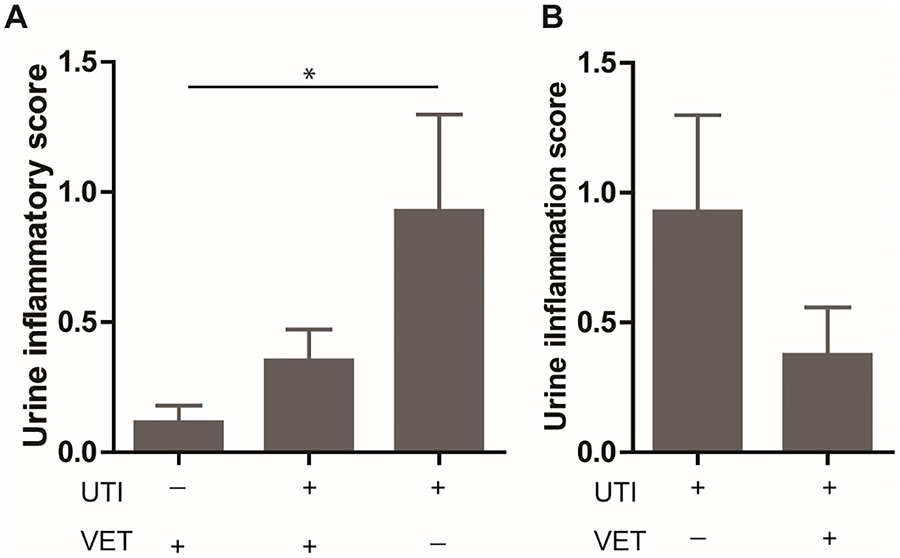
Figure 2. Postmenopausal women with a history of recurrent UTI not on vaginal estrogen therapy display increased inflammatory cell influx in the urine.
Representative samples from each group. (A) At baseline, patients with rUTI demonstrate significantly higher urine inflammation scores compared to patients without rUTI (0.93 vs 0.12). (B) Follow-up evaluation demonstrated significant decrease in urine inflammation scores after 3 months of VET in patients with rUTI (0.93 vs 0.38). rUTI, recurrent urinary tract infections; VET, vaginal estrogen therapy. Bars represent mean ± SEM. *p<0.05.