Figure 5.
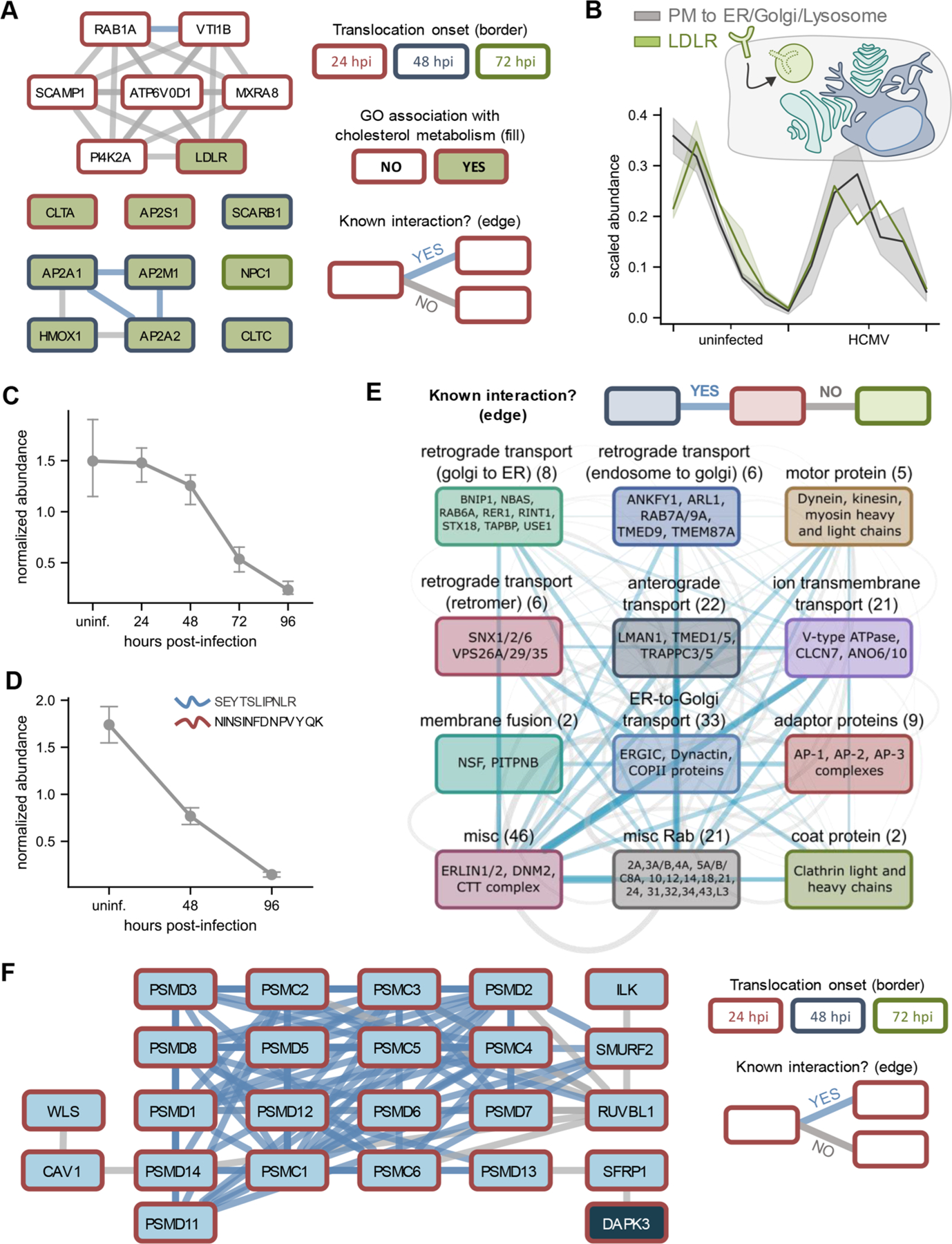
HCMV infection targets cholesterol metabolism, cellular trafficking factors, and Wnt signaling via protein translocations. (A) Translocating and co-translocating proteins involved in cholesterol metabolism. Co-translocations that correspond to a known interaction are shown in blue, while other co-translocations are shown in gray. Node border color denotes the time of translocation onset. (B) Translocation profiles of LDLR relative to the synthetic translocation profiles generated for plasma membrane (PM) to ER/Golgi/Lysosome movements. (C) LDLR protein levels decrease throughout HCMV infection. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates. (D) Validation of decrease in LDLR levels by targeted mass spectrometry. Error bars represent the standard deviation across two unique LDLR peptides quantified by parallel reaction monitoring (PRM). (E) Translocating and co-translocating protein categories involved in intracellular trafficking. Edge width scales with the number of TRANSPIRE-identified co-translocations that represent known (blue) or unknown (gray) associations. (F) Translocating and co-translocating proteins involved in Wnt signaling.
