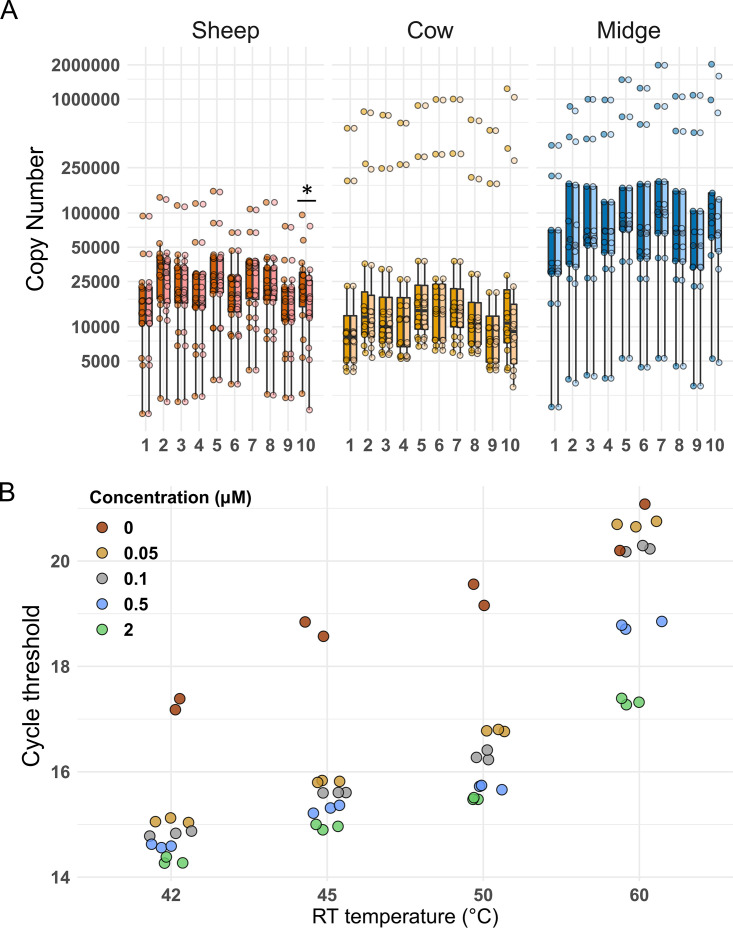
FIG 1.
(A) Influence of primer-independent cDNA amplification on segment copy number (CN) in each host. CN values are colored according to host species, with lighter coloring for CN values after correction for primer-independent cDNA amplification. The correction consisted of subtracting the copy number yielded in an RT-qPCR assay without a primer in the RT step, and it was done for each segment and sample. Segment numbers appear at bottom. The asterisk indicates the only segment-host combination (segment 10 in sheep) for which a significant difference was detected between the uncorrected and corrected CNs. (B) Influence of temperature and primer concentration at the RT step on primer-independent cDNA amplification and qPCR sensibility. Data presented were obtained with the RT-qPCR assay for segment 10, the segment showing significant primer-independent amplification. RNA extracted from BTV-infected BHK cells was used as the template. RT-qPCRs were carried out as described in the text. Colors follow final primer concentration (μM) in RT step 1. Red dots indicate PCR output when RT was performed without a primer. The experiment was performed with two or three biological replicates. We selected an RT temperature of 42°C and a primer concentration of 2 μM.