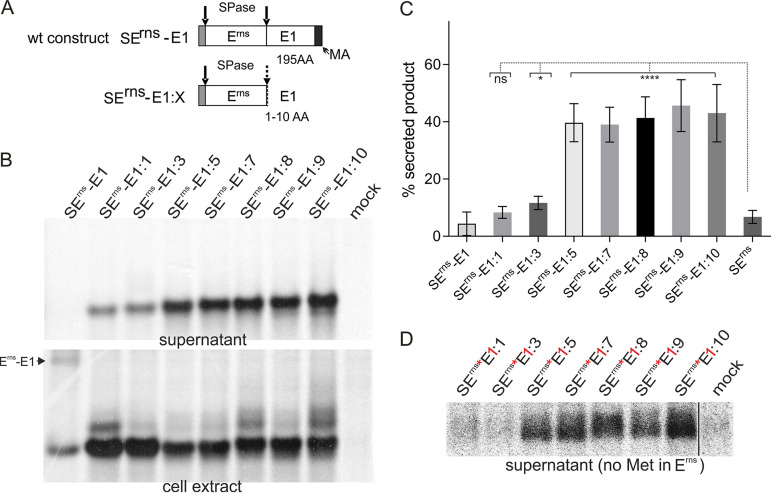
FIG 4.
Very short E1 extensions at the Erns carboxy terminus lead to increased secretion of the precursor protein. (A) Schematic representation of the constructs. (B) PAGE of proteins precipitated from the supernatant or extracts of cells transiently expressing the indicated viral proteins. The precipitation products were treated with PNGase F before electrophoresis. (C) Diagram summarizing the results of at least three independent immunoprecipitation experiments quantified by phosphorimager analysis. The bars represent the amount of secreted proteins as percent of total recovered expression product. For calculations, the results for extra- and intracellular proteins were set to 100% expression product as the basis for calculation of the secretion value. Error bars are indicated as well as the P value of Erns with E1 extension compared to Erns without E1 (construct SErns; see Fig. 1 and 3 for PAGE pictures). ****, P < 0.0001; *, P = 0.011. Please note that secretion of full-length Erns-E1 and Erns expressed from SErnsE1was detected only after prolonged exposure time. The secretion rate determined for SErnsE1:1 was not significantly different compared to that of SErns. (D) PAGE with secretion products precipitated from supernatants of cells expressing the indicated proteins with Erns containing no methionine (indicated by red asterisk) and the first residue of the E1 moiety replaced by methionine (indicated by red “1”). The expressed protein was labeled with [35S]-methionine alone, resulting in low intensity of the bands and visible pixels. Only Erns proteins carrying a carboxy-terminal E1 extension are detected here. As indicated by the black line, the samples and the mock control were run on the same gel but not directly next to each other.