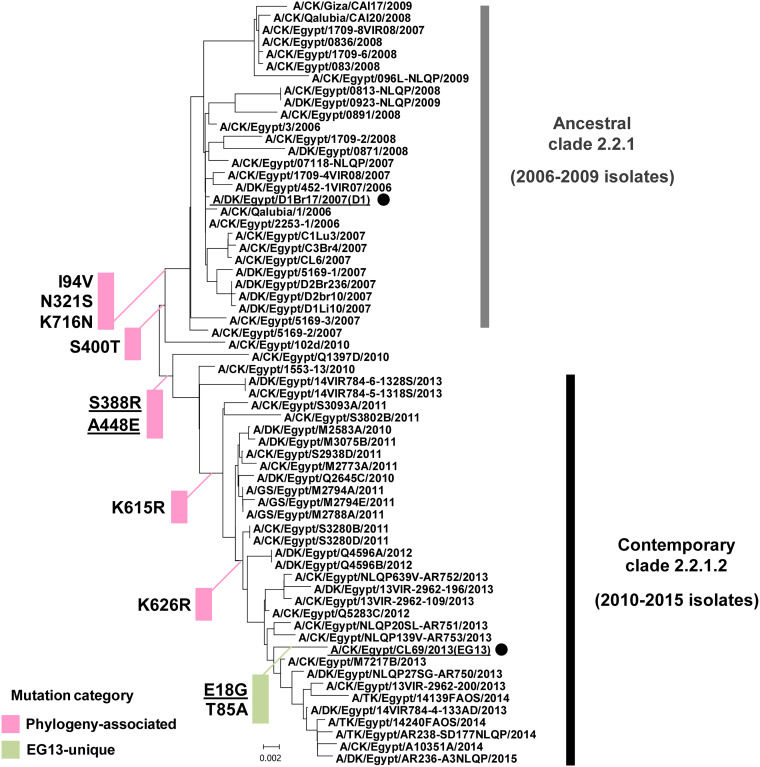
FIG 3.
Phylogeny of the PA gene in clade 2.2.1 viruses isolated in Egypt. The phylogenetic tree of the PA genes of ancestral clade 2.2.1 viruses isolated in Egypt, including the D1 virus, and of contemporary clade 2.2.1.2 viruses isolated in Egypt, including the EG13 virus, was reconstructed from the nucleotide sequences of the PA genes of the Egyptian reference strains in the GISAID database. This reconstruction used the neighbor-joining method with 1,000 bootstrap replicates and was rooted to the prototype A/quail/Hong Kong/G1/1997 (H5N1) strain. The two clade 2.2.1 strains in this study are representative ancestral (D1) and contemporary (EG13) strains and are underlined and marked with black circles. CK, DK, GS, and TK in the virus strain names denote chicken, duck, goose, and turkey hosts, respectively. The PA mutations acquired during the evolution of clade 2.2.1 viruses are shown beside each branch, with the mutations grouped into two categories, i.e., 8 phylogeny-associated mutations and 2 EG13-unique mutations. The three mutations that were shown to act cooperatively in this study to increase clade 2.2.1.2 replication are underlined.