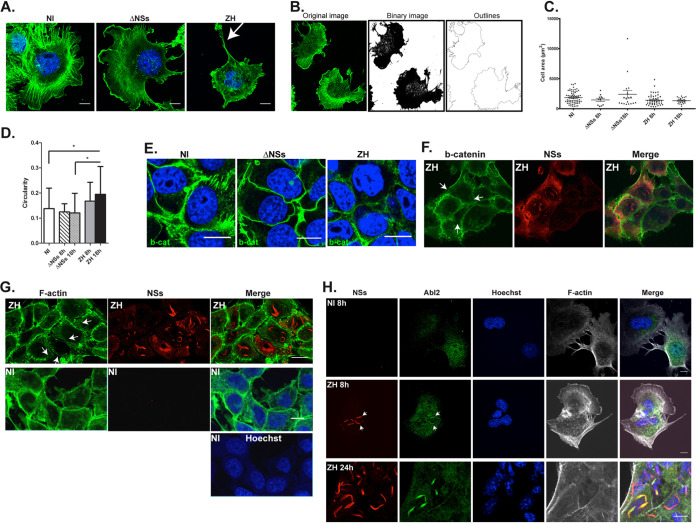
FIG 4.
Infection with the virulent ZH but not the avirulent ΔNSs strain affects cell morphology and adherens junctions. Murine hepatocytes (AML12 cell line) either noninfected (NI) or infected with the avirulent ΔNSs or the virulent ZH strains of RVFV were labeled at 8 h (A, B, F, and H) and 18 h (E, G, and H) p.i. using a DNA intercalating agent to visualize the nucleus (Hoechst, in blue), phalloidin to visualize filamentous actin (F-actin in green or gray in A, B, G, and H), an anti-NSs antibody (NSs, in red), an anti-beta-catenin antibody (b-cat in green in E and F), and an anti-Abl2 (Abl2 in green in H). White arrows indicate long F-actin-rich extensions in (A), dissolution of adherens junctions in (F) and (G), and colocalization of Abl2 with NSs in (H). (B) The analyze particle function of ImageJ software was used to transform the images into binary images and determine the cell outlines. (C and D) Main parameters such as the cell area and perimeter were determined and cell shape was analyzed by calculating the circularity = 4π × (area/perimeter2). Results, from a minimum of 2 independent experiments for each condition, correspond to the average of n = 70 cells analyzed for NI; n = 11 for ΔNSs at 8 h p.i.; n = 18 for ΔNSs at 18 h p.i.; n = 48 for ZH at 8 h p.i.; and n = 21 for ZH at 18 h p.i. Data are means ± SD. Significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA test with Dunnett correction with ΔNSs and ZH compared to NI and ΔNSs compared to ZH. P value: *, <0.05. Images correspond to single confocal sections. Bar = 10 μm.