FIGURE 5.
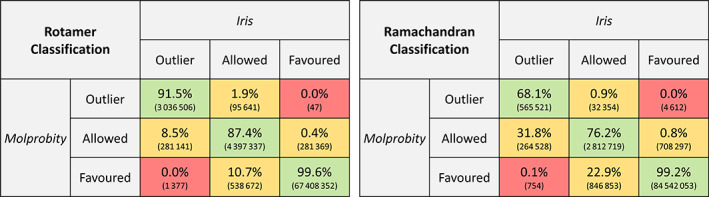
Confusion matrices for Ramachandran (left) and rotamer (right) classification agreements between Iris and MolProbity. Figures in brackets are the number of residues. Percentages are given as a proportion of the sum of each Iris classification. In the case of rotamer classifications, discrepancies between MolProbity and Iris arise as a result of the different formats of the reference data; MolProbity has access to the entire original dataset, allowing for very accurate interpolation for each case, whereas the compression Iris uses to store the reference data yields slightly less precise classifications, especially at the interfaces between classifications (i.e., borderline cases). Discrepancies in the Ramachandran classifications are partly due to the differing interpolation methods applied by MolProbity and Clipper, but more significantly to the fact that the thresholds are arbitrary; and those selected for iris are the ones that are used in Coot, to facilitate the transition between an Iris report and the Coot validation tools. These are not necessarily the same as those used by MolProbity
