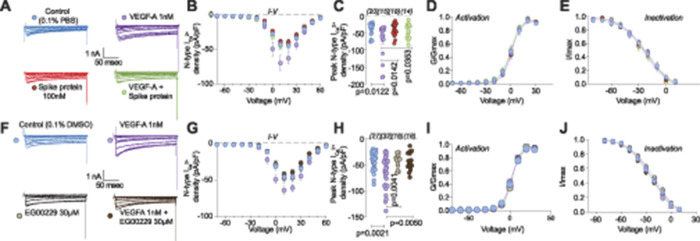
Figure 4.
Vascular endothelial growth factor-A(VEGF-A)-mediated increase in calcium currents is normalized by spike protein or neuropilin-1 receptor (NRP-1) inhibition in dorsal root ganglia neurons. Representative traces of calcium current through N-type channels (A and F) recorded from small-sized DRG neurons, incubated for 30 minutes with the indicated treatments, in response to holding voltage of −60 mV with 200-ms voltage steps applied at 5-s intervals in +10 mV increments from −70 to +60 mV. Pharmacological isolation of N-type (Cav2.2) current was achieved with a cocktail of toxins/small molecules. Summary of current–voltage curves (B and G) and normalized peak (C and H) currents (pA/pF) from dorsal root ganglia neurons as indicated. Boltzmann fits for normalized conductance (G/Gmax) voltage relationship for voltage-dependent activation (D and I) and inactivation (E and J) of the sensory neurons as indicated. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. Half-maximal activation and inactivation (V1/2) and slope values (k) for activation and inactivation were not different between any of the conditions (P > 0.9999, Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn post hoc); values presented in Table S2, http://links.lww.com/PAIN/B190. P values of comparisons between treatments are as indicated; for full statistical analyses, see Table S1, http://links.lww.com/PAIN/B190.