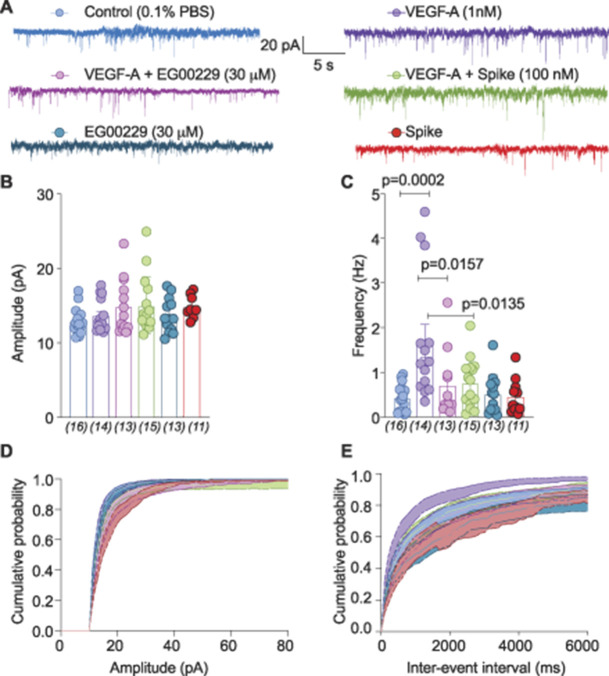
Figure 5.
Spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current frequency is reduced by spike protein or pharmacological antagonism of neuropilin-1 receptor (NRP-1) by EG00229. (A) Representative traces of sEPSC from neurons of the substantia gelatinosa in the superficial dorsal horn (lamina I/II) treated for at least 30 minutes with the indicated conditions. Summary of amplitudes (B) and frequencies (C) of sEPSCs for all groups is shown. Cumulative distribution of the sEPSC amplitude (D) and the interevent interval (E) recorded from cells as indicated. Perfusion of 30 μM EG00229 decreased spontaneous excitatory synaptic transmission (A–E) in lumbar dorsal horn neurons. P values of comparisons between treatments are as indicated; for full statistical analyses, see Table S1, http://links.lww.com/PAIN/B190. sEPSC, spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current.