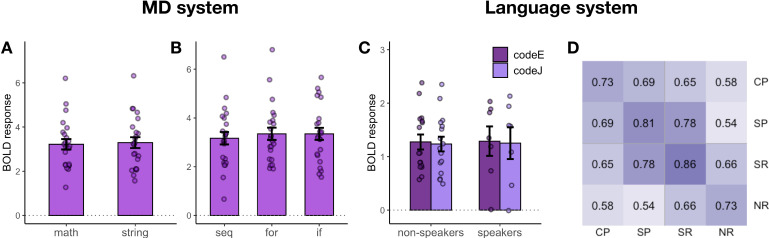
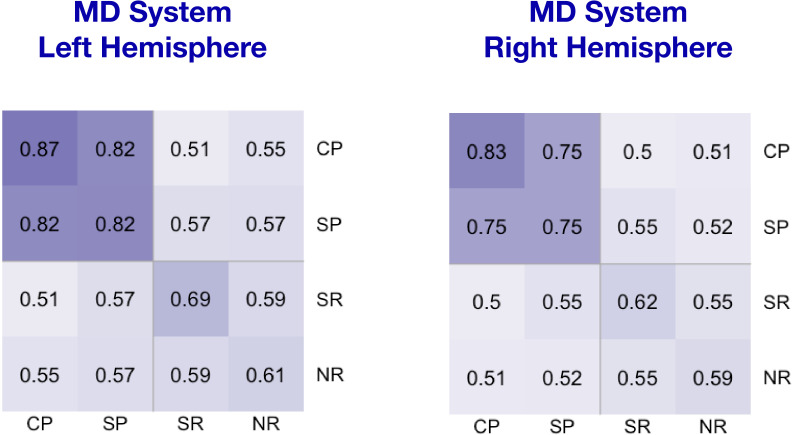
Figure 4. Follow-up analyses of responses to Python code problems.
(A) MD system responses to math problems vs. string manipulation problems. (B) MD system responses to code with different structure (sequential vs. for loops vs. if statements). (C) Language system responses to code problems with English identifiers (codeE) and code problems with Japanese identifiers (codeJ) in participants with no knowledge of Japanese (non-speakers) and some knowledge of Japanese (speakers) (see the ‘Language system responses...' section for details of this manipulation). (D) Spatial correlation analysis of voxel-wise responses within the language system during the main task (SP – sentence problems and CP – code problems) with the language localizer conditions (SR – sentence reading and NR – nonwords reading). Each cell shows a correlation between the activation patterns for each pair of conditions. Within-condition similarity is estimated by correlating activation patterns across independent runs.