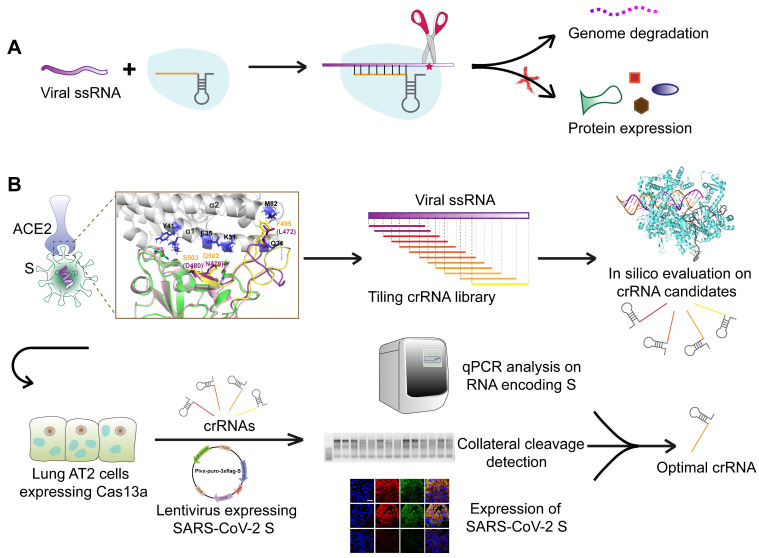
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the design of the SARS-CoV-2-targeting CRISPR-Cas13a-based tool. A. The cleavage mechanism of CRISPR-Cas13a complex on viral single-strand RNA. The complementary segment in the crRNA sequence targets specific ssRNA and the hairpin-like non-complementary segment is involved in the binding of the crRNA to Cas13a. Following the activation of Cas13a, the target viral RNA is cleaved. The collateral cleavage effect results in the degradation of the viral genome and non-target mRNAs. B. Schematic representation of the identification of a specific SARS-CoV-2 target, and the design and screening of crRNA candidates. Bioinformatics analyses were used to identify a specific RNA segment in SARS-CoV-2 S, followed by designing a tiling crRNA library targeting this specific RNA segment. In-silico evaluation was performed to screen potential optimal crRNA candidates. The S RNA knockdown efficiency and collateral cleavage effect were examined in HepG2 and AT2 cells to identify an optimal crRNA.