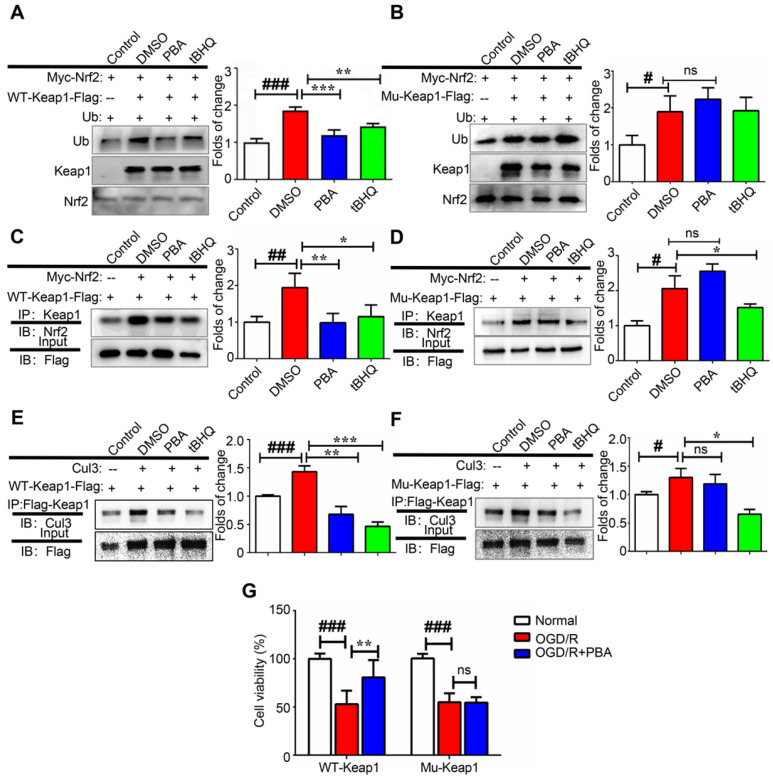
Figure 6.
PBA suppresses Keap1-mediated ubiquitination of Nrf2 by disrupting the interaction between Cul3 and Keap1. (A and B) PBA suppressed Nrf2 ubiquitination in a Keap1-Cys77 and C434-dependent manner. First, 293T cells were transfected with WT-Keap1 or C77S and C434S-Keap1, Myc-Nrf2, and Ub plasmids for 24 h and treated with 30 μM PBA. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-Myc beads, and the ubiquitination level was evaluated using the anti-Ub antibody. (C and D) PBA induced the dissociation of the Nrf2-Keap1 complex. Then, 293T cells were cotransfected with WT-Keap1 and Flag-Nrf2 plasmids for 24 h and treated with 30 μM PBA for 12 h. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with the anti-Flag antibody, and the level of Nrf2 was assessed using the anti-Nrf2 antibody. (E and F) PBA disrupted the interaction between Cul3 and Keap1. The 293T cells were transfected with the WT-Keap1 or C77S-C434S-Keap1 plasmids for 24 h and treated with 30 μM PBA for 12 h. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with the anti-Flag antibody, and the level of Cul3 was measured using the anti-Cul3 antibody. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, the control vs DMSO; *p < 0.05,**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, PBA or tBHQ vs DMSO. (G) C77S and C434-Keap1 mutant blocked the protective effect of PBA against OGD/R-induced primary mouse cardiomyocytes injury. Primary mouse cardiomyocytes were transfected with mouse WT-Keap1 or C77S and C434S-Keap1 mutant vectors. After 24 h, the cells were treated with the indicated doses of PBA and subjected to OGD conditions as described in the Method section for 3 h and under normal conditions for another 18 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT assays. #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001, the control vs OGD/R; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, OGD/R+PBA vs OGD/R.