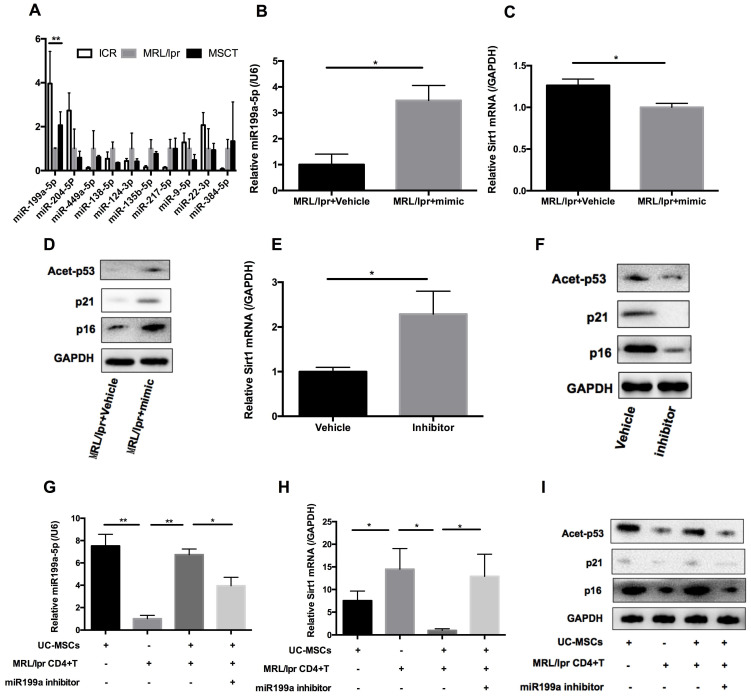
Figure 5.
hUC-MSCs induced miR-199a-5p can increase MRL/lpr splenic CD4+ T cell senescence. (A) qPCR analysis of the levels of ten potential miRNAs in WT mice, PBS-treated MRL/lpr mice and hUC-MSCs-treated MRL/lpr mice splenic CD4+ T cells. (B-D) qPCR and western blotting analysis of the levels of miR-199a-5p, Sirt1, p21, p16 and acetyl-p53 in vehicle and miR-199a-5p mimic-treated MRL/lpr splenic CD4+ T cells. (E-F) qPCR and western blotting analysis of the levels of Sirt1, p21, p16 and acetyl-p53 in vehicle and miR-199a-5p inhibitor-treated WT splenic CD4+ T cells. (G-I) MRL/lpr splenic CD4+ T cells and hUC-MSCs were cultured alone or together in the presence or absence of miR-199a inhibitor using a transwell system. MiR-199a-5p, Sirt1, p21, p16 and acetyl-p53 were quantified in hUC-MSCs (the first bar) or splenic CD4+ T cells (the last three bars). GAPDH was used as a protein loading control. All experimental data were verified in at least two independent experiments. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.