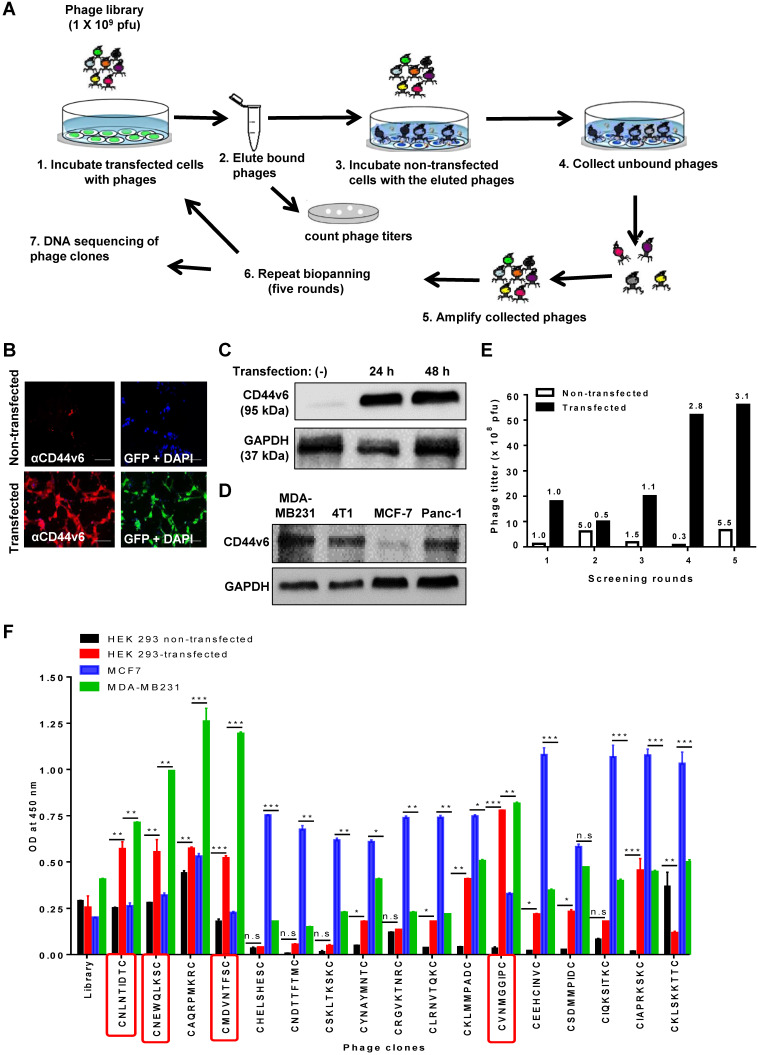
Figure 1.
Screening of a phage peptide library and phage cell-binding ELISA to identify CD44v6-binding peptides. (A) Experimental schemes for phage peptide library screening. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of CD44v6 with an anti-CD44v6 antibody (red) in HEK 293T cells transfected or not with a GFP-tagged CD44v6 expression vector (green). DAPI was used for nuclear staining (blue). Scale bars = 40 µm. (C) Western blotting analysis of CD44v6 expression in non-transfected (-) and transfected HEK 293T cells at 24 and 48 h after transfection. (D) Western blotting analysis of CD44v6 expression in tumor cells. (E) Enrichment of phage titers during screening rounds. After each round, the phage titers (plaque-forming units; pfu) were measured by plaque assays. Numbers represent the fold ratios relative to the first round. (F) The phage cell-binding ELISA of individual phage clones was performed using HEK 293T cells transfected or not with a CD44v6 expression vector, MDA-MB231 cells, and MCF7 cells. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; n.s, not significant by one-way ANOVA.