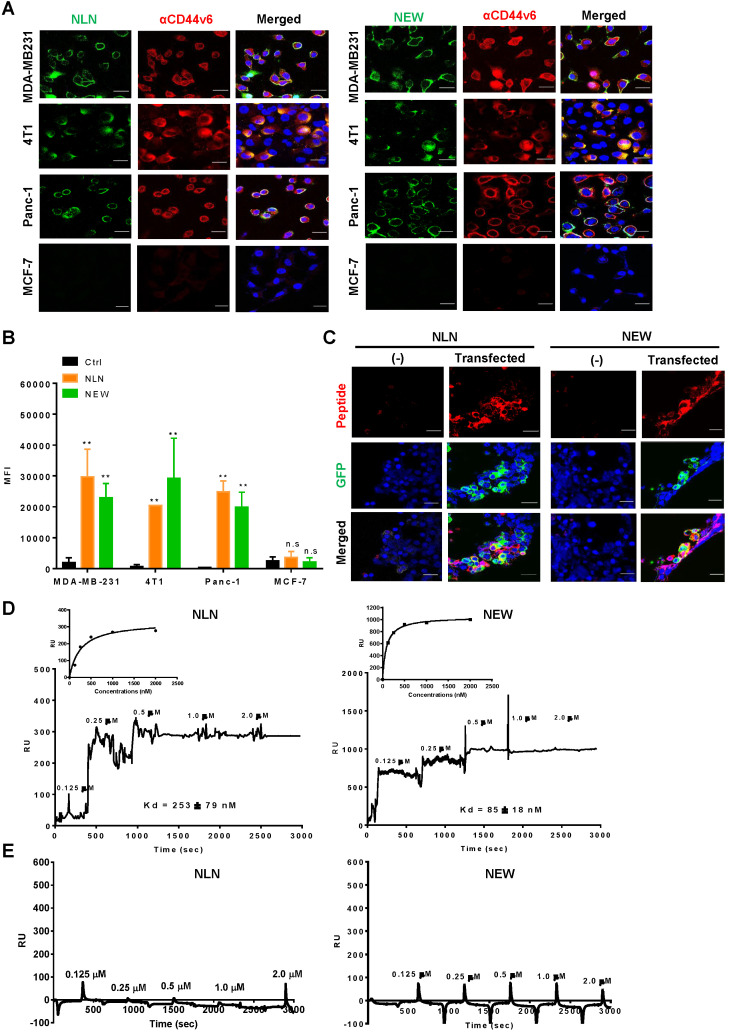
Figure 2.
NLN and NEW bind selectively to CD44v6-overexpressing cells and the CD44v6 protein. (A) Cellular binding of FITC-labeled NLN and NEW (green, 25 µM) and staining of CD44v6 (red) in CD44v6-high MDA-MB231, 4T1, and Panc-1 cells and CD44v6-low MCF7 cells. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 20 µm. (B) Mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs) of FITC-labeled NLN or NEW (25 µM) bound to MDA-MB231, 4T1, Panc-1 and MCF7 cells. Data represent the mean MFIs ± standard errors (S.E.) of peptide-bound cells from three separate experiments. **, P < 0.01; n.s, not significant compared with the control peptide (Ctrl) by one-way ANOVA. (C) Cellular binding of TAMRA-labeled NLN and NEW (red, 25 µM) and expression of CD44v6 (green) in HEK 293T cells transfected or not with a GFP-tagged CD44v6 expression vector. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 20 µm. (D-E) SPR analysis of the binding affinity (KD value) of NLN and NEW to recombinant CD44v6-Fc (D) and CD44-Fc (E) proteins. Inset are a binding plot for the peptides. RU, resonance unit.