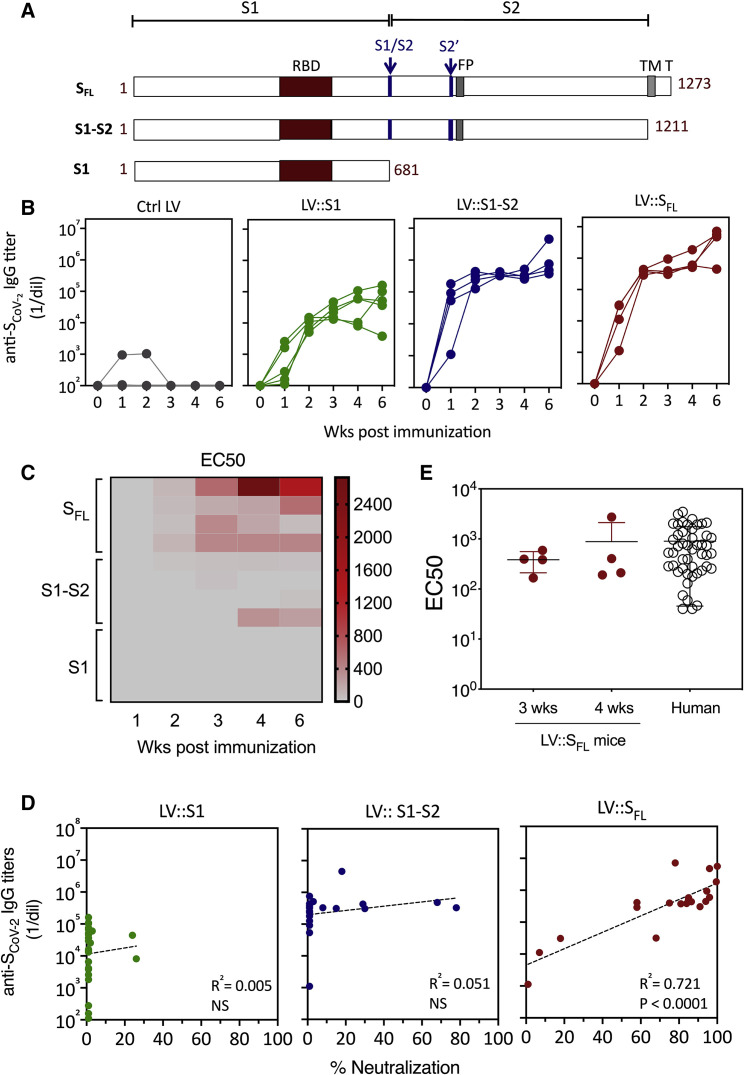
Figure 1.
Induction of anti-SCoV-2 Ab responses by LV
(A) Schematic representation of three forms of SCoV-2 protein (SFL, S1-S2, and S1) encoded by LV injected into mice. RBD, S1/S2 and S2′ cleavage sites, fusion peptide (FP), transmembrane domain (TM), and short internal tail (T) are indicated.
(B) Dynamic of anti-SCoV-2 Ab response after LV immunization. C57BL/6 mice (n = 4 per group) received an i.p. injection of 1 × 107 TU of LV::GFP as a negative control, LV::S1, LV::S1-S2, or LV::SFL. Sera were collected 2, 3, 4, and 6 weeks after immunization. Anti-SCoV-2 IgG responses were evaluated by ELISA and expressed as mean endpoint dilution titers.
(C) Neutralization capacity of anti-SCoV-2 Abs induced by LV::SFL immunization. Mouse sera were evaluated in a sero-neutralization assay for determination of EC50 neutralizing titers.
(D) Correlation between the Ab titers and neutralization activity in various experimental groups. Statistical significance was determined by a two-sided Spearman rank-correlation test. NS, not significant.
(E) Head-to-head comparison at a 1:40 dilution between mouse sera taken 3 or 4 weeks after immunization and a cohort of mildly symptomatic individuals living in Crépy-en-Valois, Ile de France. These patients did not seek medical attention and recovered from COVID-19. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM percentages of inhibition of luciferase activity. See also Figure S1.