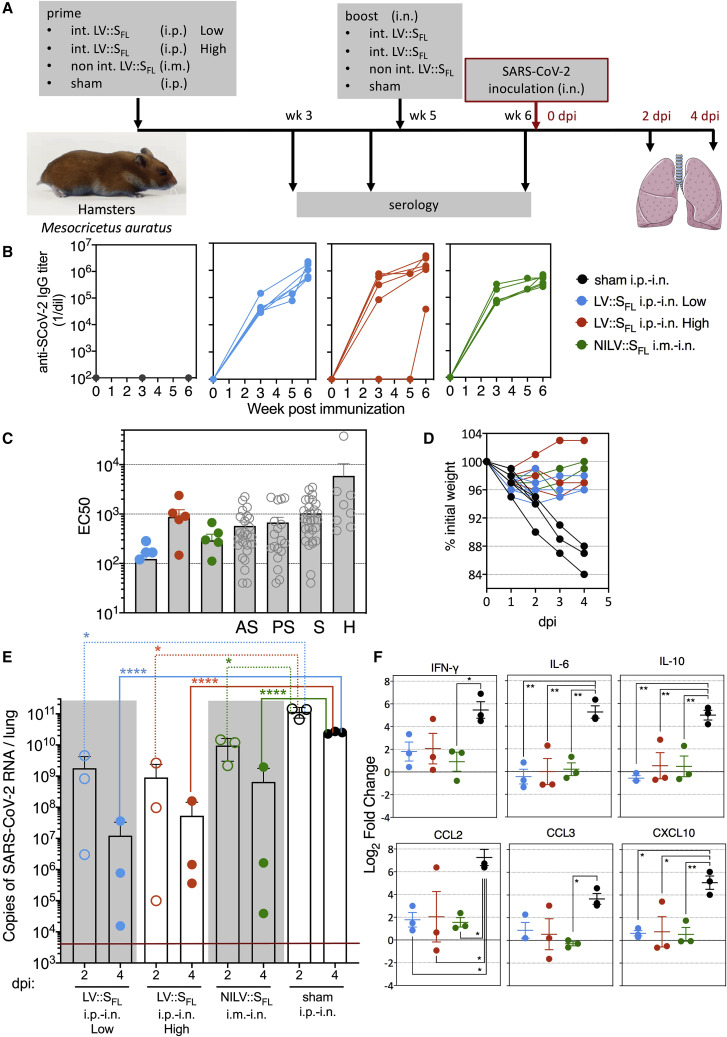
Figure 6.
Intranasal vaccination with LV::SFL strongly protects against SARS-CoV-2 in golden hamsters
(A) Timeline of prime-boost or prime-target immunization regimen and challenge in hamsters. Sham-vaccinated mice received an empty LV.
(B) Dynamic of anti-SCoV-2 Ab response following immunization. Sera were collected 3, 5 (before the boost), and 6 (after the boost) weeks after priming. Anti-SCoV-2 IgG responses were evaluated by ELISA.
(C) EC50 serum neutralizing titers after the boost or target regimen versus sera from a cohort of asymptomatic (AS), pauci-symptomatic (PS), or symptomatic (S) COVID-19 cases or of hospitalized (H) humans.
(D) Weight follow-up in hamsters either sham- or LV::SFL-vaccinated with diverse regimens. For further clarity, only the individuals reaching 4 dpi are shown. Those sacrificed at 2 dpi had the same mean weight as their counterparts between 0 and 2 dpi.
(E) Lung viral loads at 2 or 4 dpi in LV::SFL-vaccinated hamsters. Statistical significance was evaluated by a two-tailed unpaired t test; ∗p < 0.0402, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. See also Figure S4C.
(F) Relative log2 fold changes in cytokine and chemokine expression in LV::SFL-vaccinated and protected hamsters versus sham-vaccinated individuals, as determined at 4 dpi by qRT-PCR in the total lung homogenates and normalized to untreated controls. Statistical significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. See also Figures S5 and S6.