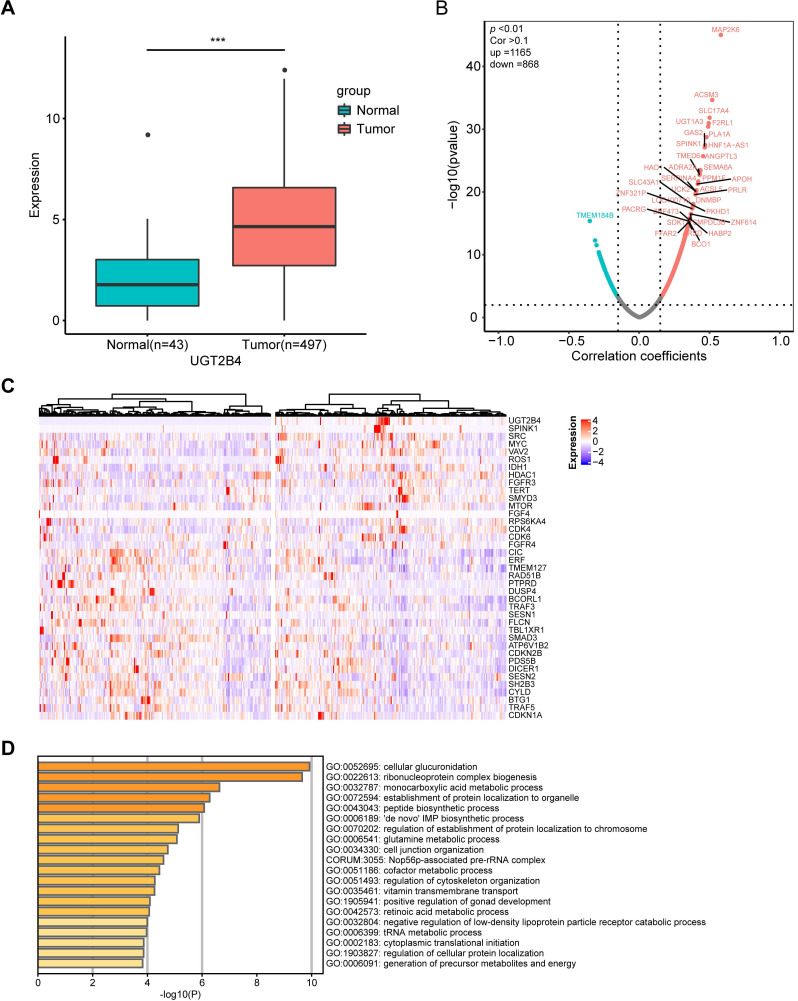
Figure 5.
Clinical and functional relevance of UGT2B4 expression in prostate cancer. A) Expression of UGT2B4 was determined in 43 normal tissue (green bar) and 497 prostate cancers (red bar) from The Cancer Genome Atlas database. UGT2B4 was found to be significantly upregulated (p<0.001) in localized prostate tumors compared with tumor-adjacent normal tissue. B) Spearman rank correlation analysis was performed on expression profiles of tumor tissues of 497 TCGA localized prostate cancer patients and UGT2B4. 1165 genes were positively co-expressed with UGT2B4 and 868 genes were negatively co-expressed with UGT2B4 i. (Spearman correlation >0.1, p<0.01). C) Thirty-seven curated oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes were correlated with UGT2B4 in the spearman rank correlation analysis. Heatmap of hierarchal clustering of patients based on expression of UGT2B4 and 37 UGT2B4 co-expressed oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes was described using a function Heatmap in ComplexHeatmap R package. Patients were split by median expression of UGT2B4 before hierarchal clustering. There was a cluster of prostate cancer patients with high expression of UGT2B4, SPINK1, and SRC. D) Functional enrichment including GO Biological Processes, KEGG, and Reactome pathways (http://www.metascape.com/) reveals that genes co-expressed with UGT2B4 in the Spearman correlation analysis were functionally enriched in ribonucleoprotein complex biogenesis, as well as glutamine, nucleotide, and monocarboxylic acid metabolic pathways.