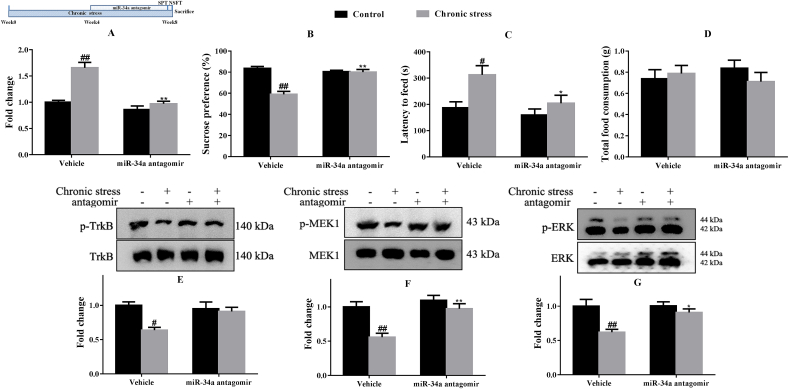
Fig. 5.
The miR-34a antagomir inhibited miR-34a expression (A), increased the sucrose preference (B), and decreased the latency to feed (C) but did not alter total food consumption (D) in mice subjected to chronic stress (n = 6 or 12). Western blots showing increases in the pTrkB/TrkB ratio (E), pMEK1/MEK1 ratio (F) and pERK/ERK ratio (G) in the hippocampus of mice treated with the miR-34a antagomir (n = 4). #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 compared with the Control-vehicle group. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared with the Chronic stress-vehicle group. Two-way ANOVA results of (A) Stress F(1,20) = 30.60, p < 0.01; Treatment F(1,20) = 35.35, p < 0.01; Interaction F(1,20) = 15.34, p < 0.01; (B) Stress F(1,44) = 31.60, p < 0.01; Treatment F(1,44) = 16.11, p < 0.01; Interaction F(1,44) = 30.08, p < 0.01; (C) Stress F(1,44) = 9.02, p < 0.01; Treatment F(1,44) = 5.79, p < 0.05; Interaction F(1,44) = 2.04, p > 0.05; (D) Stress F(1,44) = 0.23, p > 0.05; Treatment F(1,44) = 0.02, p > 0.05; Interaction F(1,44) = 1.18, p > 0.05; (E) Stress F(1,12) = 9.01, p < 0.05; Treatment F(1,12) = 2.77, p > 0.05; Interaction F(1,12) = 5.80, p < 0.05; (F) Stress F(1,12) = 16.36, p < 0.01; Treatment F(1,12) = 13.40, p < 0.01; Interaction F(1,12) = 5.19, p < 0.05; (G) Stress F(1,12) = 12.90, p < 0.01; Treatment F(1,12) = 4.86, p < 0.05; Interaction F(1,12) = 4.38, p > 0.05.