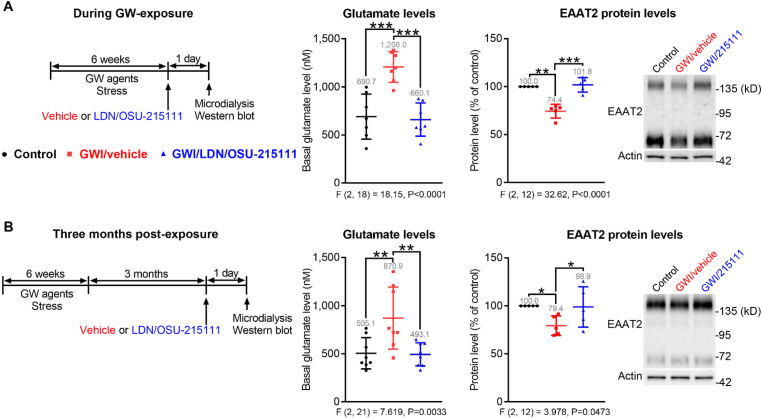
Fig. 1.
GW-exposure causes elevated extracellular glutamate levels and decreased EAAT2 protein levels in the hippocampi, which can be normalized by LDN/OSU-215111. (A) During GW-exposure. (Left) Experimental procedure. Mice were randomly divided into three groups: control, GWI/vehicle, and GWI/LDN/OSU-215111. Both GWI/vehicle and GWI/LDN/OSU-215111 mice were exposed to GW agents and stress for six weeks. On the last day of exposure, mice received a single dose of LND/OSU-215111 (10 mg/kg) or vehicle. On the next day, extracellular glutamate levels in the hippocampal CA1 area were measured by microdialysis, and hippocampal EAAT2 protein levels were examined by Western blot analysis. GW-exposed mice exhibited elevated extracellular glutamate levels (middle, n = 7) and decreased EAAT2 levels (right, n = 5), which were normalized following LDN/OSU-215111 treatment. (B) At three-months post-exposure. (Left) Experimental procedure. At three-months post-exposure, mice received LND/OSU-215111 or vehicle. On the next day, extracellular glutamate levels and EAAT2 levels were measured. GW-exposed mice still exhibited elevated extracellular glutamate levels (middle, n = 8) and decreased EAAT2 levels (right, n = 5), which were normalized following LDN/OSU-215111 treatment. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistics are based on a one-way ANOVA followed by uncorrected Fisher's LSD method for pairwise comparisons. One-sample t-test (hypothetical value = 100) was used to compare control with GWI/vehicle in Western blot analysis. F and P values for one-way ANOVA are shown. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.