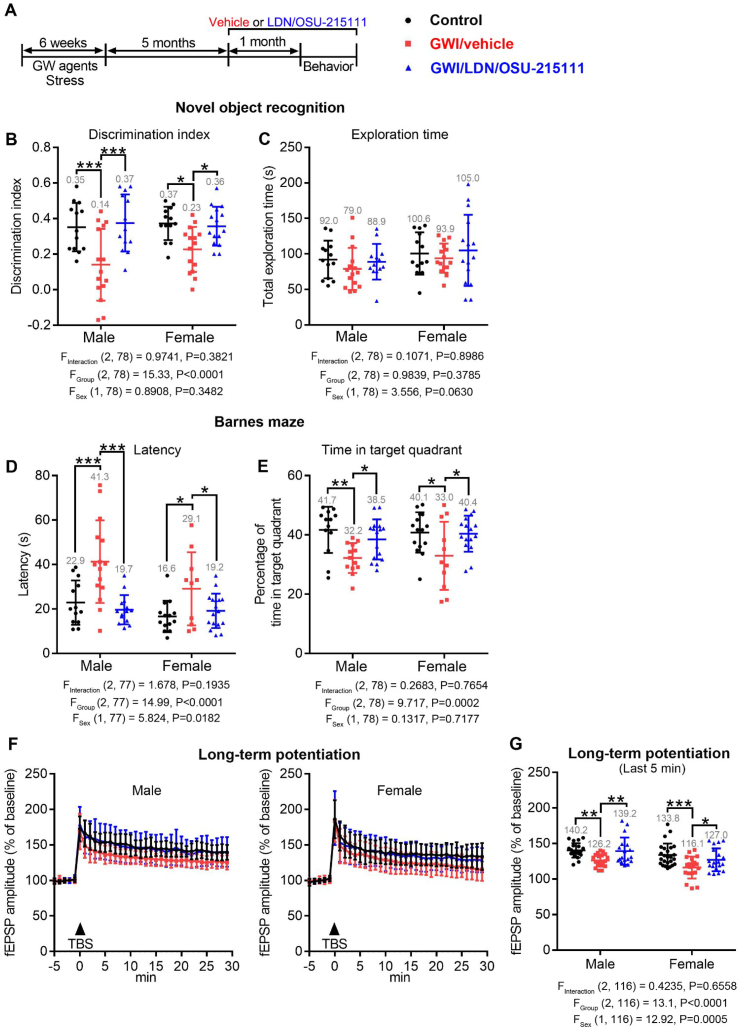
Fig. 5.
LDN/OSU-215111 normalizes cognitive impairments at five months post-GW exposure. (A) Experimental procedure. Littermate-matched mice were randomly divided into three groups: control, GWI/vehicle, and GWI/LDN/OSU-215111. Both GWI/vehicle and GWI/LDN/OSU-215111 mice were exposed to GW agents and stress for six weeks. At five-months post-exposure, GWI/LDN/OSU-215111 mice received LDN/OSU-215111; control and GWI/vehicle mice received vehicle for one-month. Subsequently, behavioral tests were conducted. (B–E) Assessment of cognitive functions. Both male and female GWI/vehicle mice exhibited significant memory deficits. LDN/OSU-215111 treatment significantly improved cognitive functions. The probe trial results of Barnes Maze were presented in D-E. n = 16–25 males and n = 15–27 females each group. (F–G) LTP assessment. GWI/vehicle mice showed a significant decrease in fEPSP LTP, and LDN/OSU-215111 treatment normalized LTP. LTP was performed on CA1 apical dendrites. n = 18–21 sections, 4–7 mice per group for males; n = 19–25 sections, 4–5 mice per group for females. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistics are based on a two-way ANOVA comparison followed by uncorrected Fisher's LSD method for pairwise comparisons. F and P values for two-way ANOVA are shown. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.